关系数据库最关键是要了解关系模型
要理解一个数据模型要从三个方面去理解数据模型:
-
数据结构
-
数据操作
-
完整性约束
-
Relational Data Structure
-
Fundamental Relational-Algebra-Operations
-
Additional Relational-Algebra-Operations
-
Extended Relational-Algebra-Operations
-
Null Values
-
Modifications of the Database
Relational-Algebra-Operations 关系代数
Relational Data Structure
采用数学上的关系来定义 Mathematics define a relation to be a subset of a Cartesian product(笛卡尔积) of a list of Domains:
Formally, given sets relation r is a subset of . Thus a relation is a set of n-tuples where 但又有所不同的是,
- 笛卡尔乘积的有限的子集
- 数据库的关系满足交换律,给每个域命名为属性
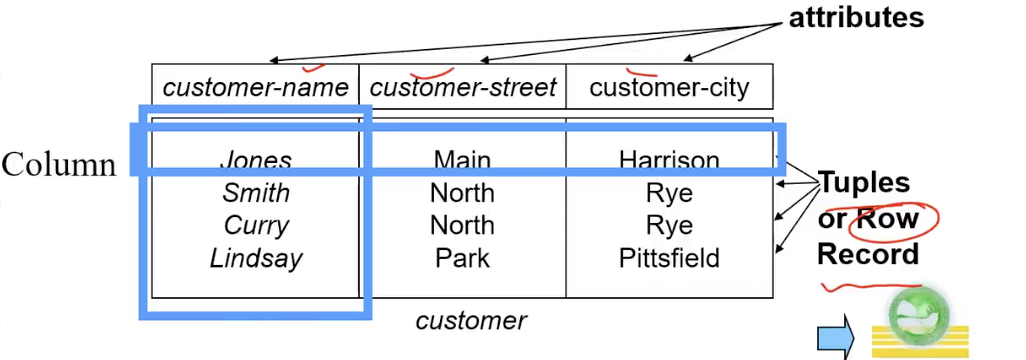
Example
if
customer-name = {Jones, Smith, Curry, Lindsay} customer-street = {Main, North, Park} customer-city = {Harrison,Rye,Pittsfield}Then r =
{(Jones,Main,Harrison), (Smith,North,Rye), (Curry,North,Rye), (Lindsay,Park,Pittsfield),...}is a relation over customer-name X customer-street X customer-city
Relation Schema(关系模式)
实际上就是对关系的抽象描述
- are attributes, each attribute of a relation has a name; The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain of the attribute,
- is a relation schema E.g. Customer-schema = (customer-name, customer-street, customer-city)
r(R) is a relation on the relation schema R E.g. customer(Customer-schema)
Relation Instance 关系实例就是在关系模式下一个具体的取值
- Order of tuples is irrelevant(无关紧要的)
- Order of attributes is irrelevant;
- For all relations, the domains of all attributes be atomic(原子性);
- Attributes names must be different;属性不能重(无法唯一确定)
- Several attributes can have the same domain;
- Tuples are not duplicate.
Superkey(超键)
R(U) is a relation schema, K is a superkey for R: for any r, no two distinct tuples have the same values on K. That is, if t1 and t2 are in r and , then ; values for K are sufficient to identify a unique tuple of each possible relation r(R) by “possible r” 使用这个属性集合去取值能取得独一无二的tuples.
Candidate Key(候选键)
A candidate key of an entity set is a minimal superkey(最小的超键) 对于这个属性集合而言,把任意一个属性去掉,都不能满足唯一性。 能够保证唯一性最小的属性集合。 E.g. 学号+姓名是超键,但不是候选键;学号是候选键。 定义超键是为了定义候选键。
Although several candidate keys may exist, one of the candidate keys is selected to be the primary key(主键、关键字)
Two Properties of Candidate Key:
- UniqLandueness(唯一性)
- No legal value of R ever contains two distinct tuples with the same value for K;
- Irreducibility(最小性)
- No proper subset of K has the uniqueness property.不可减少,任何一个真子集都不满足唯一性
Forign Key(外键)
抽象数据之间的关联关系
For R1, R2, R1 includes the Primary key X of R2, X is called a Foreign Key(外键) referencing R2; R1 is called the referencing relation of the foreign key dependence; R2 is called the referenced relation of the foreign key;
E.g. Employee(no, name, sex, age, deptno) dept(deptno, name, address)
外键不是根据名称来判断的,而是在定义的时候说明的,外键在两个表中的属性的名称可以不同,但一般一致。
外键可能发生在一张表中,一个属性参考本表中的另一个属性。 E.g. 一个班级的班长
完整性约束
Integrity Constraint of Primary Key:(实体完整性约束) Each specified column of primary key is assumed to be NOT NULL. 主键的取值不能为空,因为需要唯一定位。
Referential Integrity constraint:(参照完整性约束) The FK-values in any tuple of relation rl1 are either NULL or must appear as the PK-values of a tuple of relation r2. 外键的取值要么为空,要么等于所参照的某个主键的取值。
User-defined Integrity(用户定义完整性约束) 针对某一具体关系数据库的约束条件,它反映某一具体应用所涉及的数据必须满足的语义要求。主要包括非空约束、唯一约束、检查约束、主键约束、外键约束。
Relation Algebr(关系代数)
Six basic operators
- Select(选择)
- Project(投影)
- Union(并)
- set difference(差)
- Cartesian product(笛卡尔乘积)
- Rename(更名) The operators take one/two or more relations as inputs and give a new relation as a result.
Select notation: p is called the selection predicate
Define as :
where p is a formula in propositional calculus consisting of terms connected by :
Each term is one of: G <attribute> op <attribute> or <constant> where op is one of: E.g.
选择操作就是打开一张表,然后在这张表中找到所有满足条件的记录。
Project
Notation:
where are attribute names and r is a relation name.
- The result is defined as the relation of k columns obtained by erasing the columns that are not listed.
- Duplicate rows removed from result, sincer relations are sets.
将需要的列投影出来并去重
后面课程缺了…