History
File System
Cons:
文件系统进行数据管理,相同的数据会在不同的地方存储多次,导致冗余(redundancy),会造成数据的不一致(Inconsistent)。
并发控制问题,以及Recovery System(恢复系统)
- Data redundancy and inconsistency
- Difficulty in accessing data
- Data isolation — multiple files and formats
- Integrity problems
- Atomicty of updates(原子性修改)
- Concurrent access by multiple users
- Security problems
DBMS
pros:
- Data can be shared
- Redundancy can be reduced(由数据模型造成的冗余无法避免)
- Inconsistency can be avoided(to some extent)
- Transaction support can be provided
- Integrity can be maintained
- Security can be enforced
- …
NoSQL ⇒ No only SQL
关系数据库还是主流的数据库
三级模式结构(Three-level Architecture)
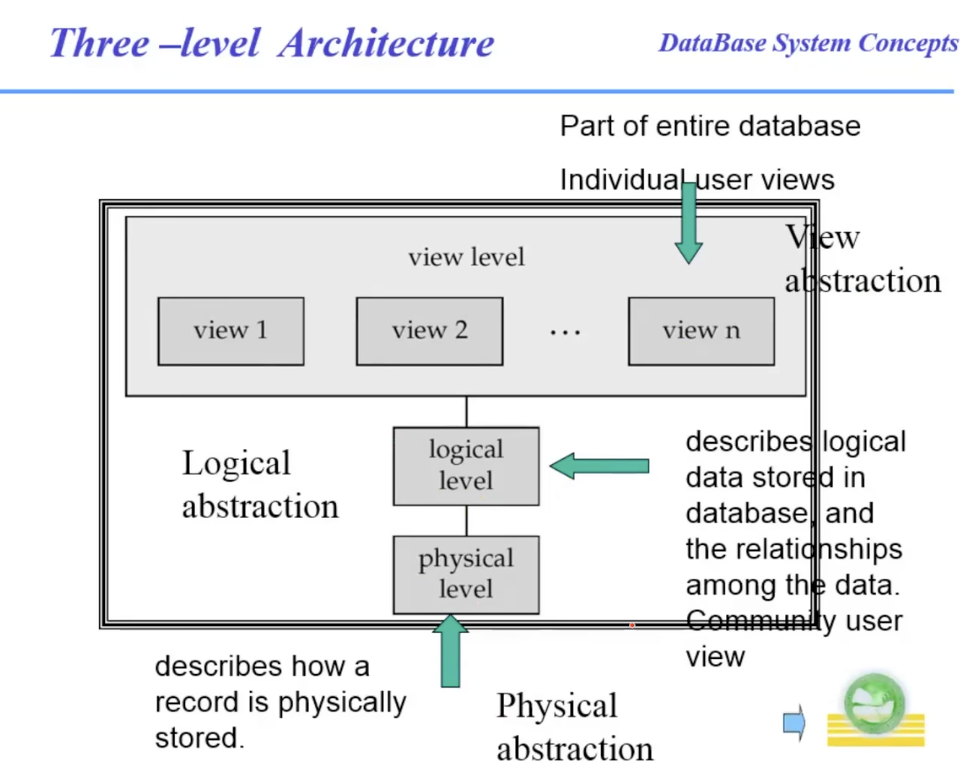 Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data.
Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data.
type customer = record
customer_id : string;
customer_name:string;
customer_street:string;
customer_city:integer;
end;需要定义Mappings
- The Physical(internal)/Logical(conceptual) mapping
- The View(external)/Logical(conceptual) mapping
三级模式,两级映像
Data Independence(数据独立性)
独立性是指:结构改,应用可以不改,有利于应用的维护
Physical Data Independence(物理数据独立性) 完备的(一定可以实现)
物理数据发生改动的时候,前端的应用可以不改动
the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema or the views (The Physical(internal)/Logical(conceptual) mapping)
Application programs need not be rewritten if the physical schema changes.
数据在磁盘上如何存储是由DBMS管理的,程序不需要了解
Logical Data Independence(逻辑数据独立性)
the ability to modify the logical schema without changing the logical views (The View(external)/Logical(conceptual) mapping)
当数据的逻辑结构改变时,用户程序也可以不变,并非能保证所有程序一定可以不改动,所以是不完备的
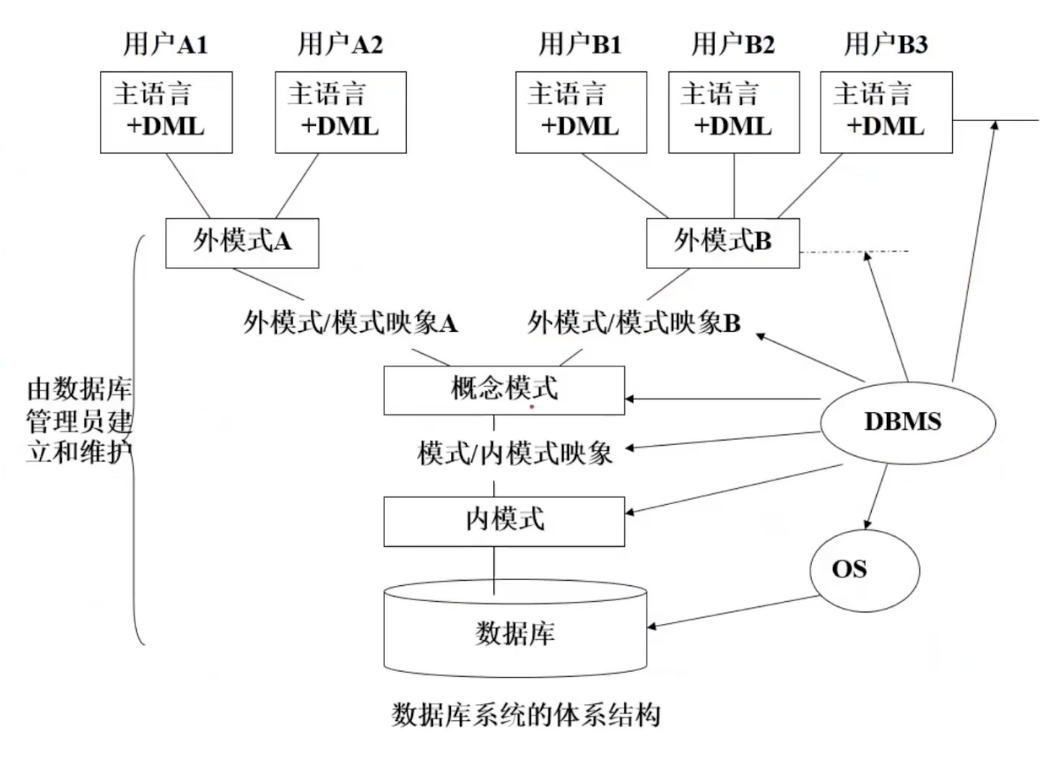
Instances and Schemas
Schema(模式) - the description of the structure of the data in a database 结构
Instance(实例) - the actual content of the database at a partiacular point in time 包含数据,动态变化的,在每一个具体时刻的取值
Data Models 数据模型
A collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics(语义), and consistency constrains(完全性约束).
- Data Structure(Core)
- Data Operations
- Constraint Rules
基于对象的数据模型 Object-based data model:
- ER Model(对象-关系型数据库模型)
- Object-oriented Model(面向对象数据模型)
基于记录的数据模型 Record-based data model:
- hierarchical(分层) data model
- network data model
- relational data model
Database Language
Data Definition Language(DDL)
Specification notation for defining the database schema;
E.g.:
Create table account(
account-number char(10),
balance integer)
)Data Manipulation Language(DML)对数据的操作语言
增删改查,SQL,非过程语言
数据控制语言 (Data Control Language)
对数据访问权进行控制的语句
Database Users
- End Users:
- naive Users
- casual users
- Application Programmeers --- Procedural SQL, Transaction
- Database analyzer and designer ----- Data modeling, Normalization theory…
- Database Administrators,DBA ----- Database maintenance, Security, Integrity, Recovery
- Database Management System designer and implementer ----- Implementation technique of above techniques for Special and New Database Management System
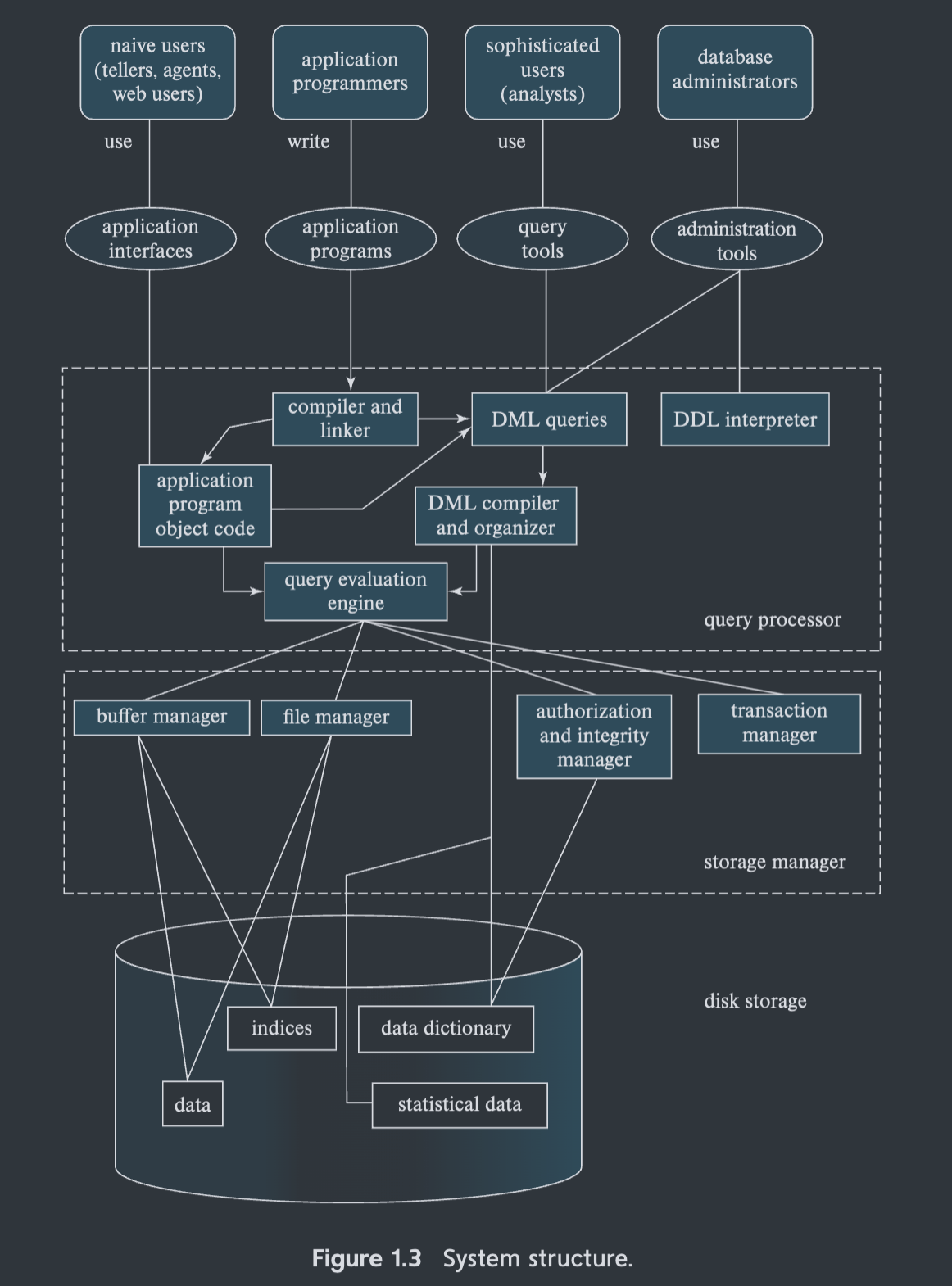
data dictionary 数据字典 元数据,整个数据库的相关信息---三级模式信息,每一步运行都需要用到数据字典的信息(meta data)元数据
Functions of DBMS
- Data Definition and storage management;
- Data Manipulation, Data Access;
- Data Security and integrity;
- Transaction management, Data recovery and concurrency;
- Data dictionary;
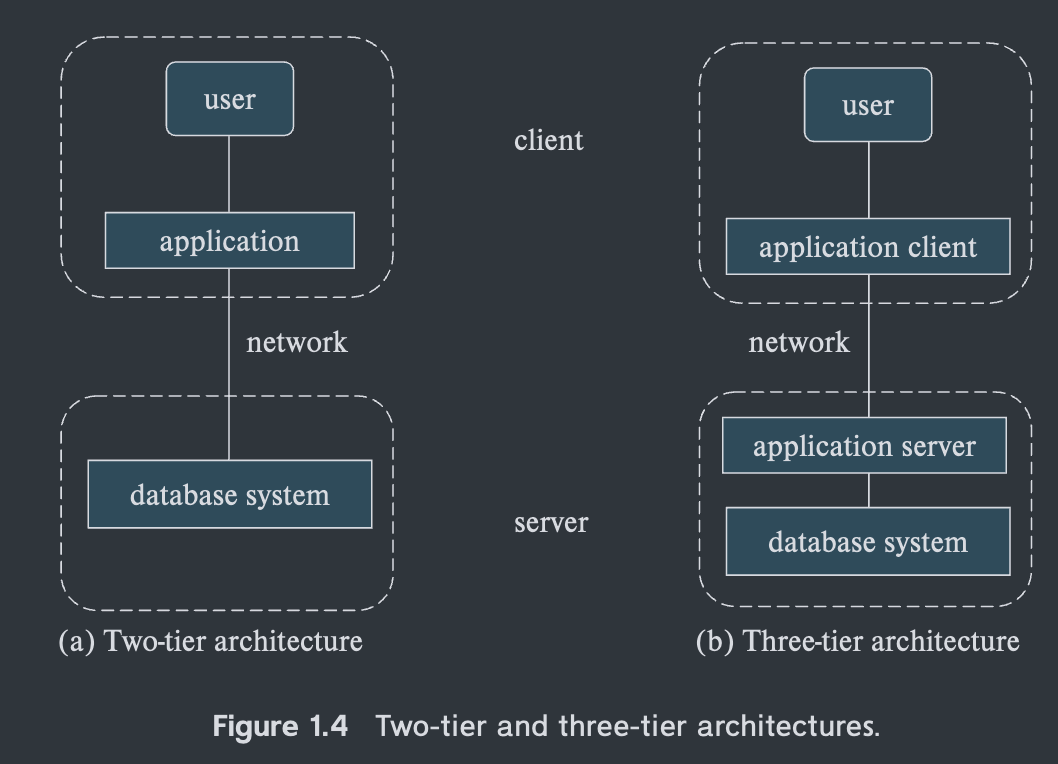
Application Architectures
C/S 结构
胖客户端结构 → B/S 结构(Browser/Server,浏览器/服务器模式) 也是C/S结构,三层结构
B/S 既简单,也容易维护