Relation Algebra
Select
Def: selects tuples that satisfy a given predicate.
Notation:
p is called the selection predicate
E.g.
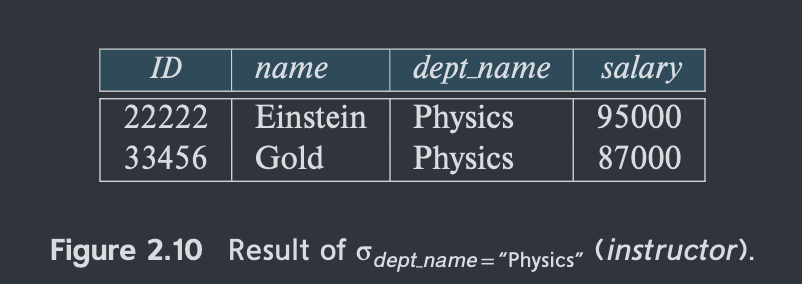 allow comparisons like
allow comparisons like
Combine several predicates into a larger predicate by using connectives:
E.g.
Project
Def: returns its argument relation, with certain attributes left out(被排除在外).
Notation:
where are attribute names and r is a relation name.
The result defined as k columns by erasing the columns that are not listed.
Duplicate rows removed from result, since relations are sets.(需要去重)
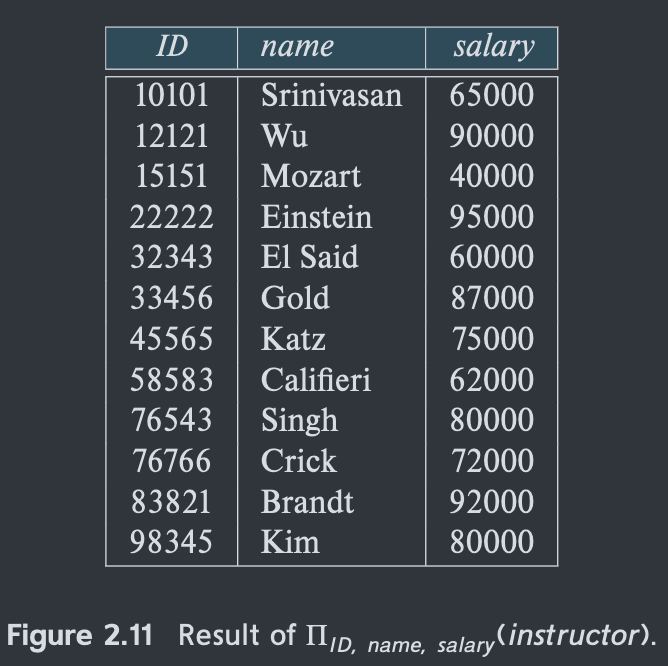 A generalized version of the operator allows expressions involving attributes to appear in the list L. For example, we could use
A generalized version of the operator allows expressions involving attributes to appear in the list L. For example, we could use
Cartesian-Product(笛卡尔积)
Cartesian-product operation(denoted by X) allows to combine information from two relations.将两个relation拼接在一起
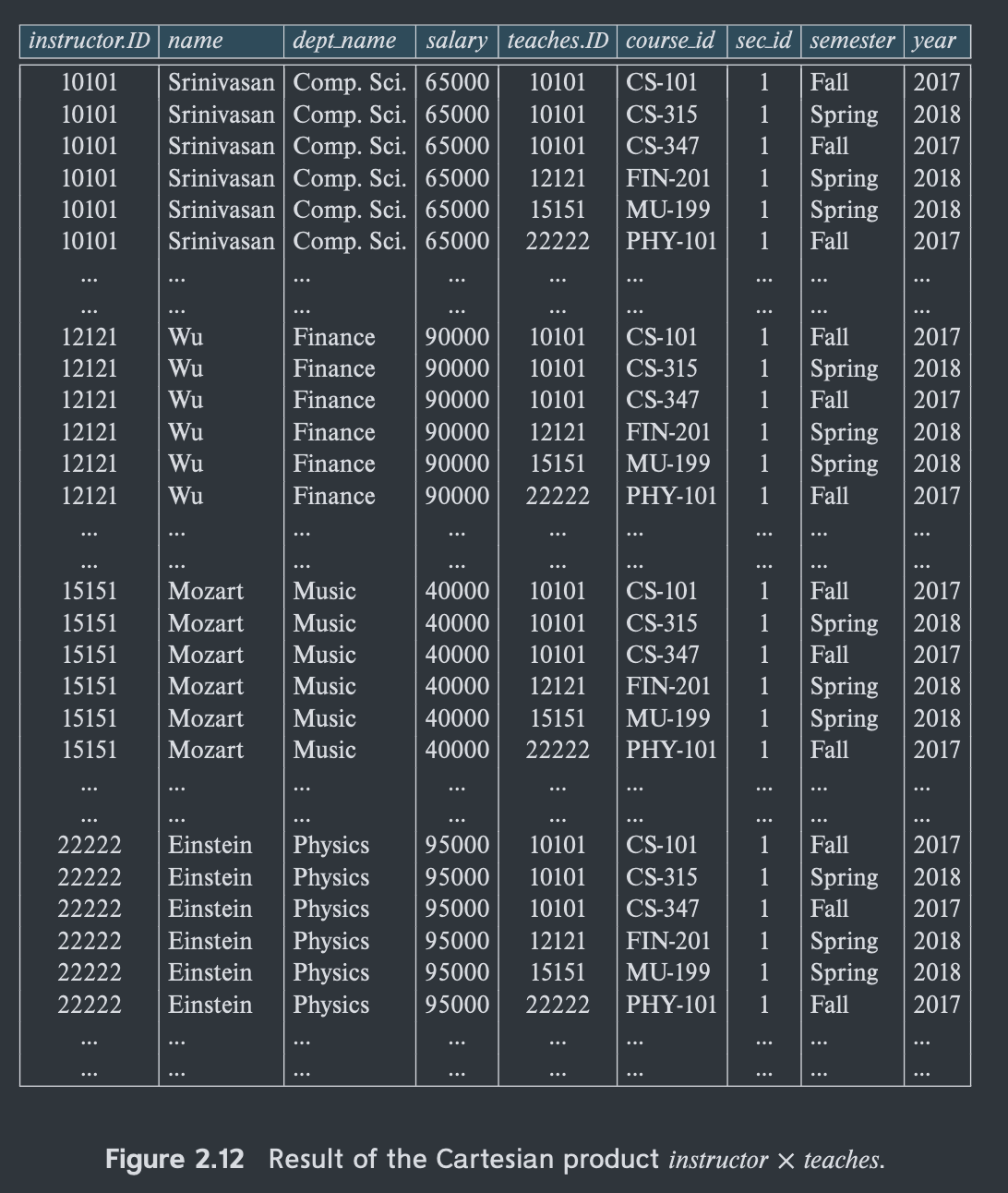 Since instructor ID appears in both relations, we distinguish between these attributes by attaching to the attribute the name of relation from which attribute originally came.
Since instructor ID appears in both relations, we distinguish between these attributes by attaching to the attribute the name of relation from which attribute originally came.
- instructor.ID
- teachers.ID
Join (连接)
The Cartesian-Product instructor X teaches associates every tuple of instructor with every tuple of teaches.将每一个元组都分别连接
Most of the resulting rows have information about instructors who did NOT teach a particular course.
but we need is that pertain to instructors and the courses that they taught, so we write
only those tuples of “instructor X teachers” that pertain to instructors and the courses that they taught.
 the picture above is the result
the picture above is the result
The join operation combine select operation and Cartesian-Product operation into a single operation.
Def:Consider relations r(R) and s(S)
Let be a predicate on attributes in schema R union S.
The join operation
Thus,
Can equivalently be written as
Union
The union operation allows us to combine two relations
Notation:
- r, s must have same arity(数量)
- The attribute domains must be compatible(相符的)
E.g.
Set-Intersection Operation
The set-intersection operation allows us to find tuples that are in both input relations. Notation:
- r, s have the same arity
- attributes of r and s are compatible

Set Difference Operation
The set-difference operation allows find tuples that are in one relation but are not in another.(差)
Notation:
Set difference must be taken between compatible relations.
- r and s must have the same arity
- attribute domains of r and s must be compatible.
E.g.

Assignment Operation
Notation:
Working like assignment in programming language
将得到的结果赋值给一个变量,有点像Go的:=
The Rename Operation
The results of relational-algebra expressions do not have a name. The rename operator is provided for a name.
Equivalent Queries
Query1
Query2
The two queries are not identical, however, they are equivalent.
Thus, we need Query optimizers.