SQL包含了对数据库的一系列操作
- DDL
- DML(Insert, Delete, Update)
- Embedded SQL(嵌入式用法)将SQL语句嵌入到其他语言中编写
- SQL实现对数据库的操作,其他的业务逻辑交给其他语言
- Dynamic SQL
- ODBC(Open Database Connectivity,开放数据库互连), JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)
- ODBC(Open Database Connectivity,开放数据库互连)提供了一种标准的API(应用程序编程接口)方法来访问数据库管理系统(DBMS)。
- JDBC是Java DataBase Connectivity的缩写,它是Java程序访问数据库的标准接口。
- Transact_SQL
Abstract
SQL is based on set and relational operations with certain mdifications and enhancements.
DDL
Create Table Construct
r is the name of the relation, each is an attribute name in the schema of relation r, is the data type of values in the domain of attribute .
E.g.
create table instructor(
ID char(5),
name varchar(20),
dept_name. varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2));var代表可变长度,括号中代表max_length
定长好维护,变长节省空间
Integrity Constraints
- not null
- primary key()
- Foreign Key () reference table r on delete restrict/cascade/set NULL
- check(P), where P is a predicate(自定义完整性约束)
create table instructor(
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2),
primary key (ID),
foreign key (dept_name) references department);当主键只有一个元素的时候,可以将primary key 直接写在对应属性的后面,外键同理。
Here is a long Example.
create table department(
dept_name varchar(20),
building varchar(15),
budget numeric(12,2),
primary key (dept_name));
create table course(
course_id varchar(7),
title varchar(50),
dept_name varchar(20),
credits numeric(2,0),
primary key (course_id),
foreign key (dept_name) references department);
create table instructor(
ID char(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
salary numeric(8,2),
primary key (ID),
foreign key (dept_name) references department);
create table section(
course_id varchar(8),
sec_id varchar(8),
semester varchar(6),
year numeric(4,0),
building varchar(15),
room_number varchar(7),
time_slot_id varchar(4),
primary key (course_id, sec_id, semester, year),
foreign key (dept_name) references course);
create table teaches(
ID char(5),
course_id varchar(8),
sec_id varchar(8),
semester varchar(6),
year numeric(4,0),
primary key (ID, course_id, sec_id, semester, year),
foreign key (course_id, sec_id, semester, year) references section,
foreign key (ID) references instructor);Domain Types in SQL

Drop and Alter Table Constructs
The drop table command deletes all information about the dropped relation from the database 是对模式的维护,将整张表连带数据一同删除,而不仅仅是对数据的操作。 所有的DDL语言是缺省提交的,不可撤回的 E.g.
DROP TABLE Shippers;The alter table command is used to add attributes to an existing relation.
where A is the name of the attribute to be added to relation r and D is the domain of A.
E.g.
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD Email varchar(255);Basic Structure of SQL Queries
A typical SQL query has the form:
-
represent attributes
-
represent relations
-
is a predicate
-
select ⇐> projection()
-
from ⇐> cartesian-product()
-
where ⇐> select()
This query is equivalent to the relational algebra expression.
select clause
An asterisk in the select clause denotes “all attributes”
select *
from instructor;The select clause may also contain arithmetic expressions involving the operators +, −, ∗, and / operating on constants or attributes of tuples. E.g.
select ID, name, salary/12
from instructor;SQL allows us to use the keyword all to specify explicitly that duplicates are not removed.
E.g.
select all dept_name
from instructor;缺省是保留重复项(all)
select distinct dept_name
from instructor;remove duplicates
where clause
条件的顺序没有关系
SQL allows the use of the logical connectives and, or, and not in the where clause. The operands of the logical connectives can be expressions involving the comparison operators <, ⇐, >, >=, =, and <>.
includes a between comparison operator.
select name
from instructor
where salary between 90000 and 100000;Tuple comparison
select name, course_id
from instructor, teaches
where (instructor.ID, dept_name) = (teaches.ID, 'Biology');instructor.ID = teaches.ID 实际上相当于连接的条件,因为from是笛卡尔积
需要注意表的前缀,要能唯一确定对应的属性
from clause
The from clause corresponds to the Cartesian-Product operation of the relational algebra.
Rename Operation
The SQL allows renaming relations and attributes using the as clause:
E.g.
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T, instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept_name = 'Comp.Sci';Keyword as is optional and may be omitted.
E.g.
S(NO,name,room_id,monitor)(学号,姓名,房间号,班长)
现在要找出和班长一个宿舍的学生的学号和姓名
需要做表的自连接
select s1.NO, s1.name
from S as s1, S as s2
where s1.room_id = s2.room_id
and s2.NO = s1.monitor
and s1.NO != s2.monitor;String Operations
percent(%).The % character matches any substring
underscore(_).The _ character matches any character
字符匹配
- ‘Intro%’ matches any string beginning with “Intro”.
- ‘%Comp%’ matches any string containing “Comp” as a substring, for example, ‘Intro. to Computer Science’, and ‘Computational Biology’.
- ’___’ matches any string of exactly three characters.
E.g.
Find the names of all instructors whose name includes the substring “dar”
select name
from instructor
where name like '%dar%';like 模糊匹配
需要使用具体语义下的% 再要进行转义
other string operations
- concatenation (using ”||”)
- converting from upper to lower case(and vice versa)
- finding string length, extracting substrings, etc.
Ordering the Display of Tuples
升序 asc 和 降序 desc
select distinct name
from instructor
order by name;Can sort on multiple attributes
order by dept_name, name,先按照第一个属性顺序排列,再按照第二个属性顺序排列
Set Operations
- The set operations union, intersect, and except operate on relations and correspond to the relational algebra operations
同样的,如果需要保留重复,可以在关键词后面加all
Aggregate Functions(聚集函数)
These functions operate on the multiset of values of a column of a relation, and return a value.
- avg: average value
- min: minimum value
- max: maximum value
- sum: sum of values
- count: number of values
E.g.
select avg (salary)
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Comp.Sci.';
-- 表中的记录数
select count (*)
from course;Group By
- Find the average salary of instructors in each department
-- 查询每个学院的平均年薪
select dept_name, avg (salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
group by dept_name;group by 可以以多个属性进行分组
Note: Attributes in select clause outside of aggregate functions must appear in group by list.
/* error */
select dept_name, ID, avg (salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name;Having Caluse
一个条件的筛选
where 是分组前对记录的筛选
having 是分组后对组的筛选,having 一定跟 group by
Note
predicates in the having clause are applied after the formation of groups whereas predicates in the where clause are applied before forming groups.
Null Values
- 值不存在
- 值不知道
select sum (salary)
from instructor;Above statement ignores null amounts
All aggregate operations except count(*) ignore tuples with null values on the aggregated attributes.
What if collection has only null values?
- count returns 0
- all other aggregates return null
Any comparison with null returns unknown
- OR:
- (unknown or true) = true,
- (unknown or false) = unknown
- (unknown or unknown) = unknown
- AND:
- (true and unknown) = unknown,
- (false and unknown) = false
- (unknown and unknown) = unknown
- NOT: (not unknown) = unknown
“P is unknown” evaluates to true if predicate P evaluates to unknown
Result of where clause predicate is treated as false if it evaluates to unknow.
Nested Subqueries(嵌套查询)
The nesting can be done in the following SQL query
as follows:
- can be replaced be a subquery that generates a single value
- can be replaced by any valid subquery
- P can be replaced with an expression of the form:
Where B is an attribute and <operation> to be defined later.
Subqueries in the Where Clause
- 相关子查询
- 无关子查询(形式上无关,即子查询可以单独执行)
select distinct course_id
from section
where semester = 'Fall' and year = 2009
and course_id in (select course_id
from section
where semester = 'Spring'
and year = 2010);in 只有在单个值比较的时候才可以使用
无关子查询先进行子查询,再进行主查询
Some Clause
select distinct T.name
from instructor as T, instructor as S
where T.salary > S.salary and S.dept
name = 'Biology'Same query using > some clause
select name
from instructor
where salary > some (select salary
from instructor
where dept_name = 'Biology')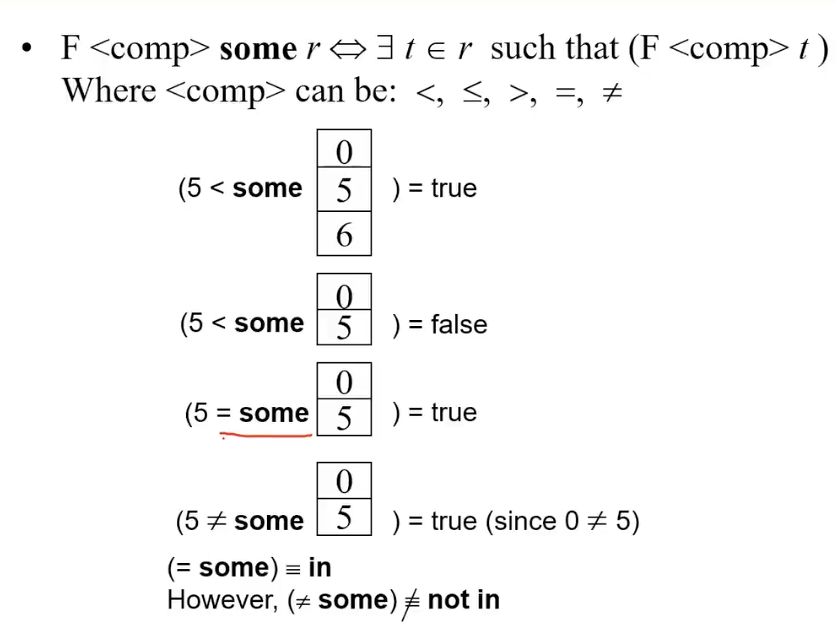
All Clause
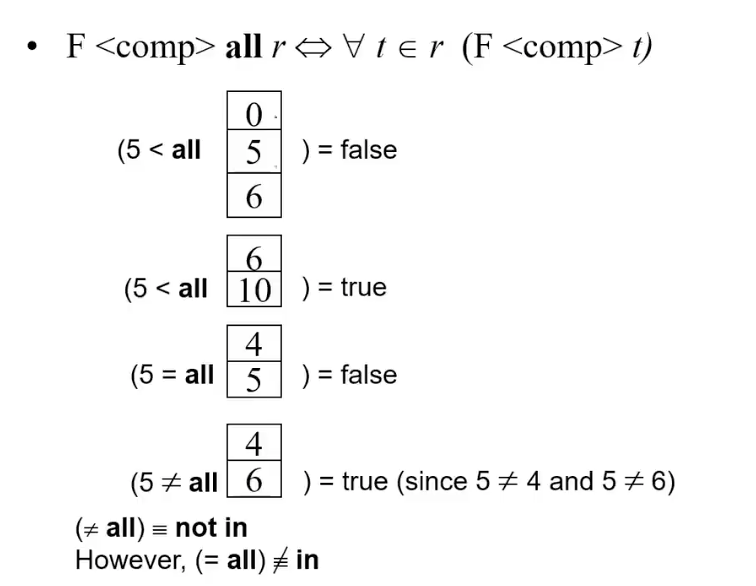
Test for Empty Relations
- The exists construct returns the value true if the argument subquery is nonempty.
- exists
- not exists E.g.
select course_id
from section as S
where semester = 'Fall' and year = 2009 and
exists (select *
from section as T
where semester = 'Spring' and year = 2010
and S.course_id = T.course_id);这是一个相关子查询,与主查询的内容有关(S.course_id)
DBMS会先从S中取一条记录,再进行子查询,循环直到结束,子查询会执行多次(效率低)
E.g.
select distinct S.ID, S.name
from student as S
where not exists ((select course_id
from course
where dept_name = 'Biology')
except
(select T.course_id
from takes as T
where S.ID = T.ID));Note that
Note: Cannot write this query using = all and its variants
子查询查询了Biology学院开设的所有除了学生选修的课之外的课程,主查询查询选择了Biology学院开设的所有课程的学生的ID和名字
可以先使用关系代数进行简化,再判断
对应的是除法操作,可以直接完成这个查询
R是选课,S是课程,Q是查询得到的学生。
学生Q和课程S的笛卡尔积都发生了选课的关系R
不使用 except
select distinct S.ID, S.name
from student as S
where not exists ((select course_id
from course
where dept_name = 'Biology')
not in
(select T.course_id
from takes as T
where S.ID = T.ID));Unique Clause
- The unique construct tests whether a subquery has any duplicate tuples in its result
- the unique construct evaluates to “true” if a given subquery contains no duplicates.
Subqueries in the From Clause
E.g.
select dept_name, avg_salary
from (select dept_name, avg (salary) as avg_salary
from instructor
group by dept_name
where avg_salary > 42000);不是使用现成的表作为操作对象,而是将子查询的结果作为操作对象
Note that we do not need to use the having clause
With Clause
The with clause provides a way of defining a temporary relation whose definition is available only to the query in which the with clause occurs.
对应的是关系代数里面的
with max_budget(value) as
(select max(budget)
from department)
select department.name
from department, max_budget
where department.budget = max_budget.valueSubqueries in the Select Clause
Scalar Subquery
Modification of the Database
Deletion
- The command : delete from
delete from instructor将instructor的所有数据删除
删除是以元组为单位删除
delete from instructor
where dept_name in (select dept_name
from department
where building = 'Watson');删除在Watson建筑的学院的所有老师信息
delete from instructor
where salary < (select avg (salary)
from instructor);先执行嵌套内的语句,即select avg (salary) from instructor得到一个值,再继续执行
Insertion
- The command :
Insert into Values()
E.g.
Add a new tuple to course
insert into course
values('CS-437','Database Systems','Comp.Sci.',4);上述的操作不写顺序有可能将数据放错,不安全的(有可能并不知道创建时候表的顺序)
下面是安全的写法
insert into course (course_id, title, dept_name, credits)
values('CS-437','Database Systems',Comp.Sci.',4);one more pro
insert into course
values('CS-437','Database Systems','Comp.Sci.',null);使用安全写法的时候,若有空值不需要写上null
insert into strudent
select ID, name, dept_name , 0
from instructorAdd all instructors to the student relation with tot_creds set to 0
Update
- The command:
Update Set
Increase salaries of instructors whose salary is over $100,000 by 3%, and all others by a 5%
update instructor
set salary = salary * 1.03
where salary > 100000;
update instructor
set salary = salary *1.05
where salary <= 100000;The order is important.每一个更新都会扫描所有的记录
Can be done better using the case statement.
Index
索引涉及到数据库的Physical(内模式),供DBS使用
CREATE INDEX H_INDEX ON STUDENT(HEIGHT)
-- 缺省是ASC
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX SC_INDEX ON SC(SNO ASC,CNO DESC)
DROP INDEX H_INDEXUNIQUE:索引文件的一条记录唯一对应数据文件的一条记录,取值需要唯一
索引可以建立在多个属性上,按顺序
索引的顺序不会影响数据文件的数据