这节课我是听的数据库第6章 关系数据理论(第二部分:范式理论 1NF-2NF-3NF) 也会有部分邓芳老师课程(英文部分)
范式理论
- 函数依赖
- 码
- 范式
- 2NF
- 3NF
- BCNF
- 多值依赖
- 4NF
- 规范化小结
范式级别表示的是这个范式的水平,级别越好,表示的越好 目标要求:
- 判断是什么范式的表
- 如何升级成更高范式的表
函数依赖
- 函数依赖的Def
- 平凡函数依赖与非平凡函数依赖
- 完全函数依赖与部分函数依赖
- 传递函数依赖
Def
定义:设R(U)是一个属性集上的关系模式,X和Y是U的子集。若对R(U)的任意一个可能的关系r(对表上的一行),r不可能存在两个元组在X上的属性值相等,而在Y的属性值不等,则称“X函数确定Y”或“Y函数依赖于X”,记作。
- 先找候选键
- 再找主属性(候选键包含的属性),区分主属性和非主属性

平凡/非平凡函数依赖
- 则称是非平凡的函数依赖
- (Sno,Cno,Grade)
- 则称是平凡的函数依赖
若,则X称为这个函数依赖的决定因素 若,则记作
完全函数依赖与部分函数依赖
Def:
在R(U)中,如果,并且对于X的任何一个真子集X’,都有,则称Y对X完全函数依赖,记作
若,但Y不完全函数依赖于X,则称Y部分函数依赖于X,记作
只需要X的部分属性(X的某个真子集)就能确定Y
题目中如何判断:
- 求出左边的真子集的闭包,看是否包含右边
传递函数依赖
Def:
在R(U)中,如果,则称Z对X传递函数依赖
Noted:如果,则Z直接依赖于X,而不是传递函数依赖
Keys and Functional Dependencies
Def:K is a superkey for relation schema R if and only if
Def:K is a candidate key for R if and only if
- for no (最小性)
DF allow constraints that cannt be expressed with superkeys.
范式
Def:符合某一种级别的关系模式的集合
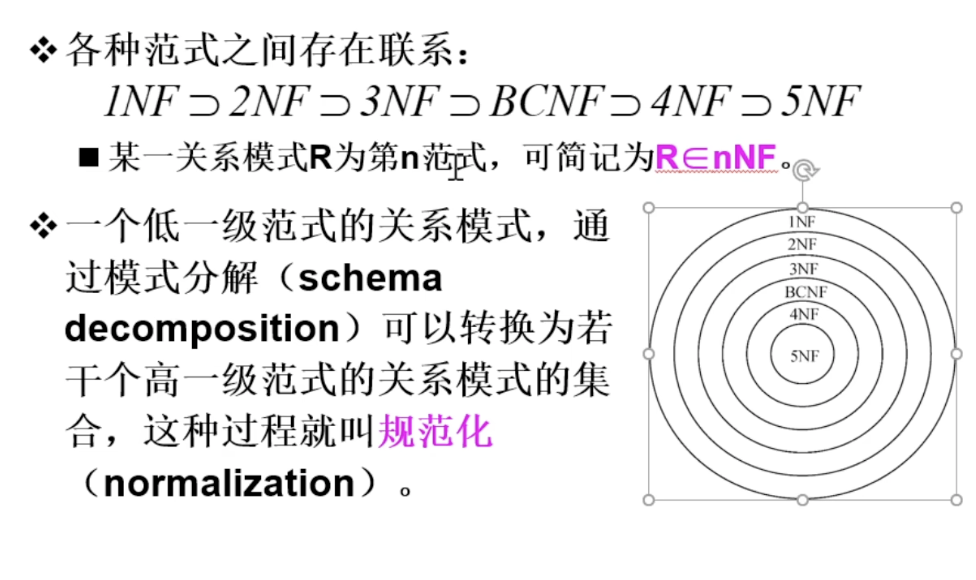 1、2、3、BC范式是函数依赖
4、5NF是多值依赖
1NF:一个表中,每个格都是不可再细分的数据项
1、2、3、BC范式是函数依赖
4、5NF是多值依赖
1NF:一个表中,每个格都是不可再细分的数据项
一个关系模式不属于3NF,会产生以下的问题:
数据冗余和增删改的异常
- 插入异常
- 如果插入一个新学生,但该学生未选课,即该生无Cno,由于插入元组的时候必须给定主键,因此插入失败
- 删除异常
- 如果S4只选了一门课C3,现在他不再选这门课,则删除C3后,整个元组的其他信息也被删除了
- 修改复杂
- 如果一个学生选了多门课,则Sdept, Sloc被存储了多次。仍哦该生转系,需要修改所有相关的Sdept和Sloc,造成修改的复杂化
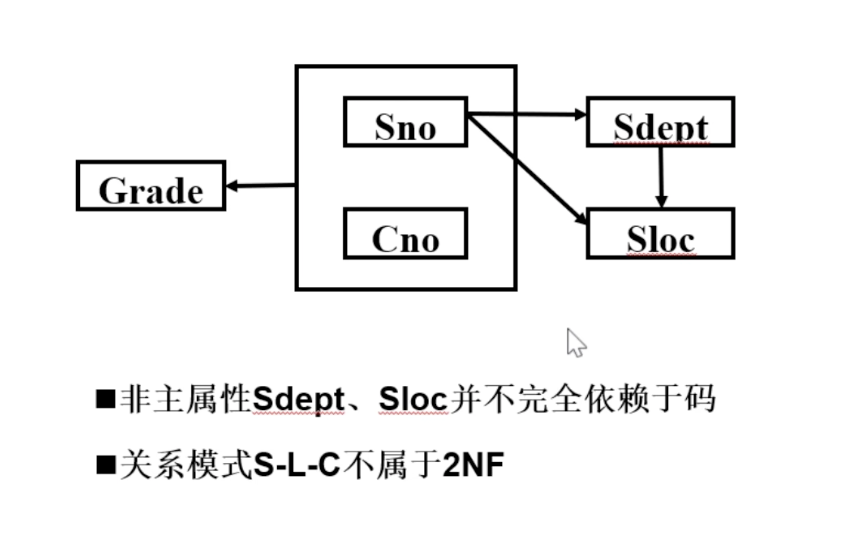
2NF
Def:若关系模式,并且每个非主属性都完全函数依赖于任何一个候选键,则
消除非主属性对主属性的部分函数依赖
即没有部分函数依赖

- 找候选键,判断主属性和非主属性
- 从主属性开始写,把所有的函数依赖关系列出来
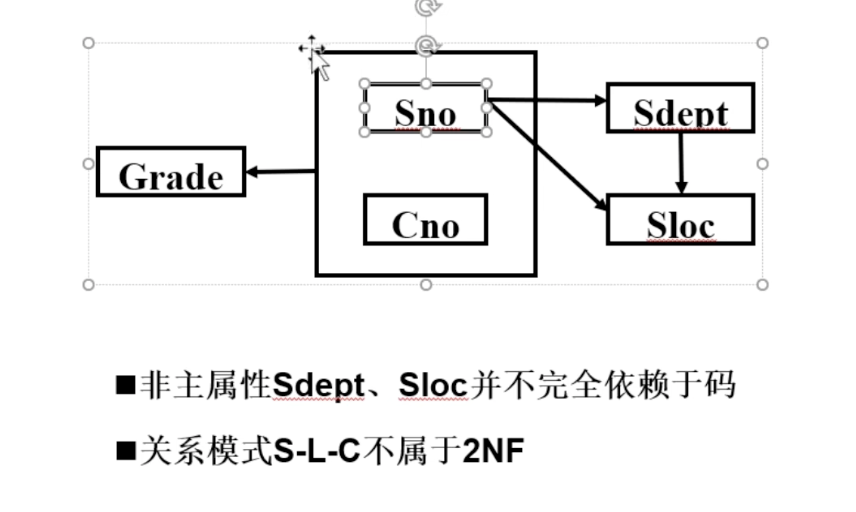
如何升级为2NF
用投影分解把关系模式S-L-C分解为两个关系模式

“谁跟你好,复制自己,把他带走”
3NF
Def:设关系模式,若R中不存在这样的键X、属性组Y以及非主属性Z(),使得成立,不成立,则称
非主属性对主属性没有传递函数依赖就是3NF
要求任意的一个函数依赖关系都要满足以下条件的一个
-
平凡依赖
-
左边是超键
-
右边是键属性
-
SC没有传递依赖,因此

BCNF
- 除了平凡依赖,左边都要是超键
Def: 设关系模式,若且时,X必含有键,则
数据依赖的公理体系
Armstrong’s Axioms
- reflexivity(自反律):
- Augmentation(增广律):
- transitivity(传递律):
可以得到三条推理规则
- 合并规则:
- 伪传递规则:
- 分解规则:
函数依赖集的闭包
- For R(U,F), The set of all functional dependencies logically implied by F is the closure of F.
- E.g. If and , then we can infer that
- We denote the closure of F by
根据F能推导出来的所有函数依赖的集合,写了的+没写的
E.g.
则
这里的闭包求法其实在大二下的形式语言与自动机已经学过了
E.g.
已知关系模式,其中
Solution:
Conclusion:,so

F的最小依赖集
Def:如果函数依赖集F满足下列条件,则称F为一个最小依赖集或者最小覆盖(离散数学下)
- F中任一函数依赖的右部仅含有一个属性
- E.g.
- F中不存在这样的函数依赖,使得F与等价
- 不存在冗余的DF,先删除看看是否能推出
- F中不存在这样的函数依赖,X有真子集Z使得与F等价
- 留下最简单的
并非唯一
函数依赖集等价 Def:如果,就说函数依赖集F覆盖G或F与G等价
两个函数依赖集等价是指他们的闭包等价
Decomposition(分解)
Decide whether a particular relation R is in “good” form.
All attributes of an original schema (R) must appear in the decomposition ():
Lossless-join decomposition(无损连接的分解)
decompose R into a set of relations {}, For all posisible relations r on schema R
A decomposition of R into and is lossless join if and only if at least one of the following dependencies is in :
E.g.
and
Dependency preservation(函数依赖保持)
decompose a relation schema R with a set of functional dependencies F into . Let be the set of dependencies that include only attributes in
E.g.
How to check if a dependency is preserved in a decomposition of R into
Code
result = while (changes to result) do for each in the decomposition t = if result contains all attributes in , then the funcitonal dependency is preserved.
E.g.
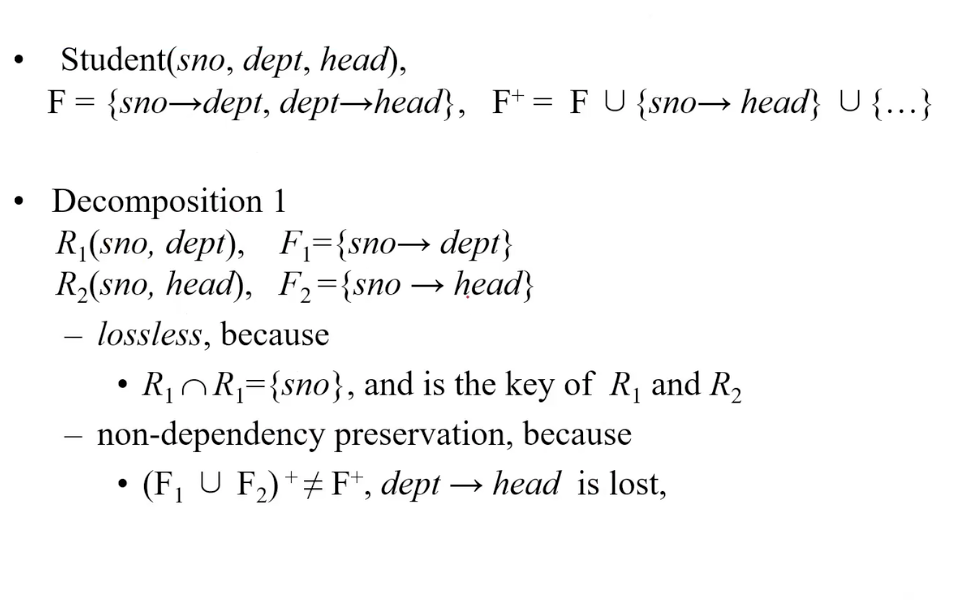
3NF Decomposition Algorithm
Code
Let be a canonical cover for F;(求F的最小函数依赖集) i:=0 for each functional dependency in do if none of the schemas , contains then begin i:=i+1; end if none of the schemas contains a candidate key for R then begin end
- 求F的最小函数依赖集
- 对于的每个函数依赖关系,如果没有任何一个已经得到的关系模式包含,则将其作为一个关系模式输出
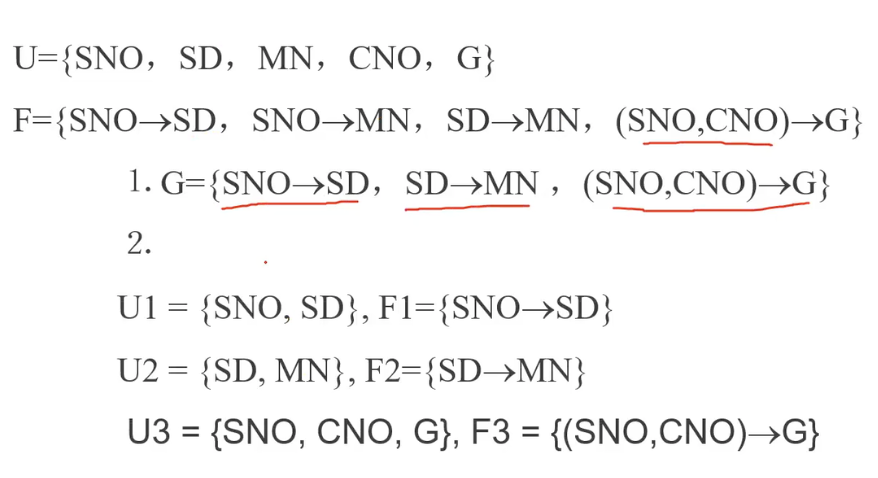 Above algorithm ensures:
Above algorithm ensures:
- each relation schema is in 3NF
- decomposition is dependency preserving
- decomposition is lossless-join
BCNF Decomposition Algorithm
Code
result:={R} done:=false compute while (not done) do if (there is a schema in result that is not in BCNF) then begin let be a notrivial functional dependency that holds on , such that is not in , and ; result:={(result - )()}{()}; end else done:=true;

没有一个通用的方法去实现函数依赖保持,只有无损连接
但是针对特定的,可以考虑去实现