- Join Expressions
- Views(外模式)
- Transactions
- Integrity Constraints
- SQL Data Types and Schemas
- Authorization
Joined Relations
Natural Join
select *
from course natrual join prereqselect *
from course join prereq on course.course_id = prereq.course_id多个表连接
List the names of students along with the titles of courses that they have taken.
select name, title
from student natural join takes, course
where takes.course_id = course.course_id;Note that takes.course_id in the where clause refers to the course_id field of the natural join result, since this field, in turn, came from the takes relation.
上面这种写法和下面的写法并不等价
select name, title
from student natural join takes natural join course;自然连接需要对应属性的值相同
the natural join of student and takes contains the attributes (ID, name, dept_name, tot_cred, course_id, sec_id), while the course relation contains the attributes (course_id, title, dept_name, credits).
只会筛选出和学生同一学院的课程,解决方法是:
select name, title
from (student natural join takes) join course using (course_id);只需要考虑course_id的匹配,用哪些属性进行连接
Inner Join
select *
from course inner join prereq on course.course_id = prereq.course_id;相比Natural Join,不会去重
Outer Join
Left/Right Outer Join
select *
from course natural left outer join prereq;
select *
from course natural right outer join prereq;
--全外连接
select *
from course natural full outer join prereq;Views
创建外模式的目的:
- 安全性
- 个性化需求
It is not always desirable for all users to see the entire set of relations in the database.
A view provides a mechanism to hide certain data from the view of certain users.
Any relation that is not of the conceptual model but is made visible to a user as a “virtual relation(虚表)” is called a view.
就像在表中建一个窗口,对外封装
A view is defined using the create view statement
create view v as < query expression > where <query expression> is any legal SQL expression.The view name is represented by v.
E.g.
create view faculty as
select ID, name, dept_name
from instructor;
select name
from faculty
where dept_name = 'Biology';视图建好后和表完全一致的,可以当成一张基表去使用
视图建好后会放到数据字典中,
Cite
Intuitively, at any given time, the set of tuples in the view relation is the result of evaluation of the query expression that defines the view. Thus, if a view relation is computed and stored, it may become out of date if the relations used to define it are modified.
To avoid this, views are usually implemented as follows: When we define a view, the database system stores the definition of the view itself, rather than the result of evaluation of the query expression that defines the view. Wherever a view relation appears in a query, it is replaced by the stored query expression. Thus, whenever we evaluate the query, the view relation is recomputed.
为了避免过时的View,所以视图定义中的查询语句一般不会触发,只有到使用这个视图的时候才会将视图的定义替换为对应的查询语句。(类似define)视图的展开
create view departments_total_salary(dept_name, total_salary) as
select dept_name, sum (salary)
from instructor
group by dept_name;由于聚集函数sum不能作为视图的属性名称,所以需要进行重命名(dept_name, total_salary),一个需要重命名,则所有属性都需要写出来命名。
View can be defined using other views
Update of View
Add a new tuple to faculty view which we defined earlier
insert into faculty values ('30765','Green','Music');This insertion must be represented by an insertion into the relation instructor, since instructor is the actual relation from which the database system constructs the view faculty.
对没有的属性赋空值(Null)
对视图的操作是不能任意进行的,比如说再定义的属性(total_salary)是无法操作的,因为无法转换成对于基表的操作。受限的更新。
只有对单张表操作,对行列的取舍,才能进行。
如果涉及到两张表,或者出现了聚集函数,则不能操作。
视图的目的是查询而不是更新。
Materialized Views(物化的视图)
Certain database systems allow view relations to be stored, but they make sure that, if the actual relations used in the view definition change, the view is kept up-to-date. Such views are called materialized views
Need to maintain the view, by updating the view whenever the underlying relations are updated.(一致性问题处理)
Transactions
- Unit of work
- Atomic transaction
- either fully executed or rolled back as if it never occurred
- Isolation from concurrent transactions
- Transactions begin implicitly
- Ended by commit work or rollback work
- But default on most databases: each SQL statement commits automatically
Commit work and Rollback work
- Commit work commits the current transaction; that is, it makes the updates per- formed by the transaction become permanent in the database. After the transac- tion is committed, a new transaction is automatically started.
- Rollback work causes the current transaction to be rolled back; that is, it undoes all the updates performed by the SQL statements in the transaction. Thus, the database state is restored to what it was before the first statement of the transaction was executed.
Integrity Constraints
On a Single Relation
- not null
- primary key
- unique
- check (P), where P is a predicate
Referential Integrity
参照完整性约束
Cascading Actions in Referential Integrity
当对主表进行操作的时候,需要满足参照完整性不被破坏
- 级联删除
- set null
- set default(no action拒绝删除)
Complex Check Clauses
subquery in check clause not supported by pretty much any database
开销大
Built-in Data Types in SQL
Index Creation
create table student(
ID varchar(5),
name varchar(20) not null,
dept_name varchar(20),
total_cred numeric(3,0) default 0,
primary key (ID));
create index studentID_index on student(ID)Indices are data structures used to speed up access to records with specified values for index attributes
select *
from student
where ID = '12345';can be excuted by using the index to find the required record, without looking at all records of student.
User-Defined Types
用户自定义类型
create type Dollars as numeric (12,2) final;
create table department
(dept_name varchar(20),
building varchar(15),
budget Dollars);Large-Object Types
Many database applications need to store attributes whose domain consists of large data items such as a photo, a high-resolution medical image, or a video.
SQL, therefore, provides large-object data types for character data (clob) and binary data (blob). The letters “lob” in these data types stand for “Large OBject.”
book review clob(10KB)
image blob(10MB)
movie blob(2GB)Granting of Privileges
Users-Roles-Privileges
Roles实际上就是权限的集合,权限→对于数据对象的操作
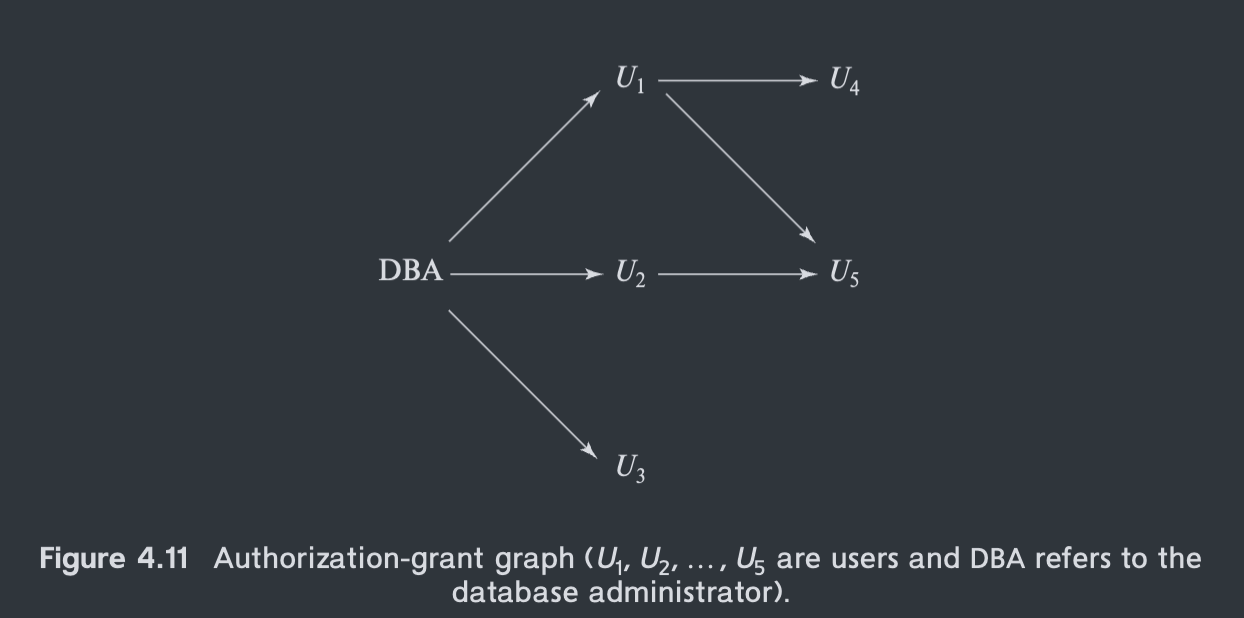
注意多重授权的权限控制
The grant statement is used to confer authorization.
grant <privilege list>
on <relation name or view name> to <user list><user list> is:
- a user-id
- public, which allows all valid users the privilege granted
- A role
-- 权限的授予
grant select on instructor to A, B, C
--权限的收回
revoke select on branch from A, B, CRoles
- create role:
grant instructor to Amit - Privileges can be granted to roles
- Roles can be granted to users, as well as others roles
create role teaching_assistant;
grant traching_assistant to instructor;Views
和对基表的授权操作同理
references privilege to creatie foreign key
grant reference (dept_name) on department to Mariano;transfer of privileges再授权
with grant option
grant select on department to Amit with grant option;级联收回和受限收回
-- 级联收回
revoke select on department from Amit, Satoshi cascade;
-- 受限收回
revoke select on department from Amit, Satoshi restrict;