FCFS SJF RR 多级反馈队列 彩票
Scheduling Concept
- Why we need scheduling? Multitasks and Concurrency.
- Scheduling is only useful when there is not enough resources.
- Preemption(抢占) is the basic assumption for fine-grained scheduling
- Either by timer interrupts or other kinds of interrupts
- Who schedules processes/threads?
- Mostly by OS
- User-level thread libraries schedule the threads by themselves
Goals
Minimize Response Time(最小化反应时间)
- Minimize elapsed time to do an operation (or job)
- Response time is what the user sees:
- Time to each a keystroke in editor
- Time to complie a Program
Maximize Throughput(最大化吞吐量)
- Maximize operations (or jobs) per second
- Throughput related to response time, but not identical;
- Two parts to maximizing throughput
Fairness(公平性)
- Share CPU among users in some equitable way
- Fairness is not minimizing average response time;
- Better average resposne time by making system less fair
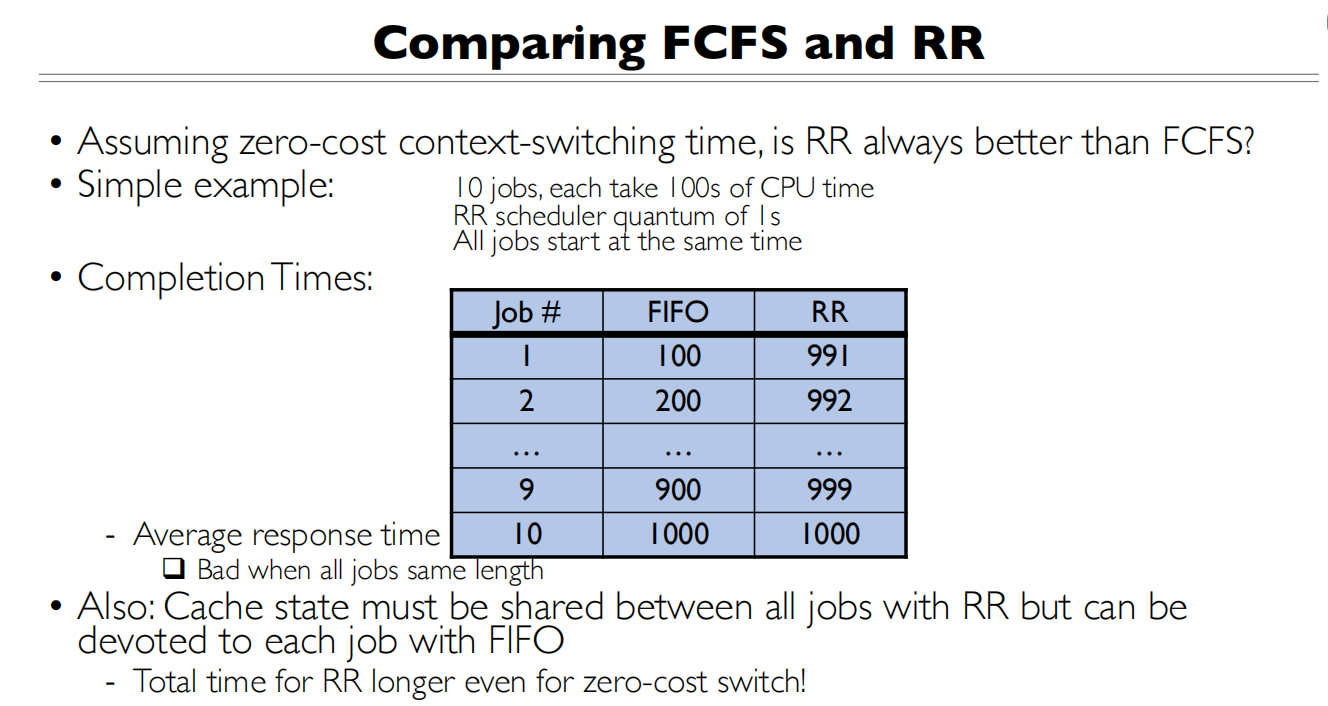
FCFS(先到先服务)
First-Come, First-Served
- Also “First In, First Out” or “Run until done”
- In early systems, FCFS meant one program scheduled until done
- Now, means keep CPU until thread blocks(线程是CPU调度的最小单元)

 问题是护航效应
问题是护航效应
 要知道怎么求
要知道怎么求
- Waiting time/Average waiting time
- Average Completion time
SJF(短任务优先)
解决了护航问题,理论上响应时间最短,但是会饥饿,而且OS也不知道任务要跑多久
RR
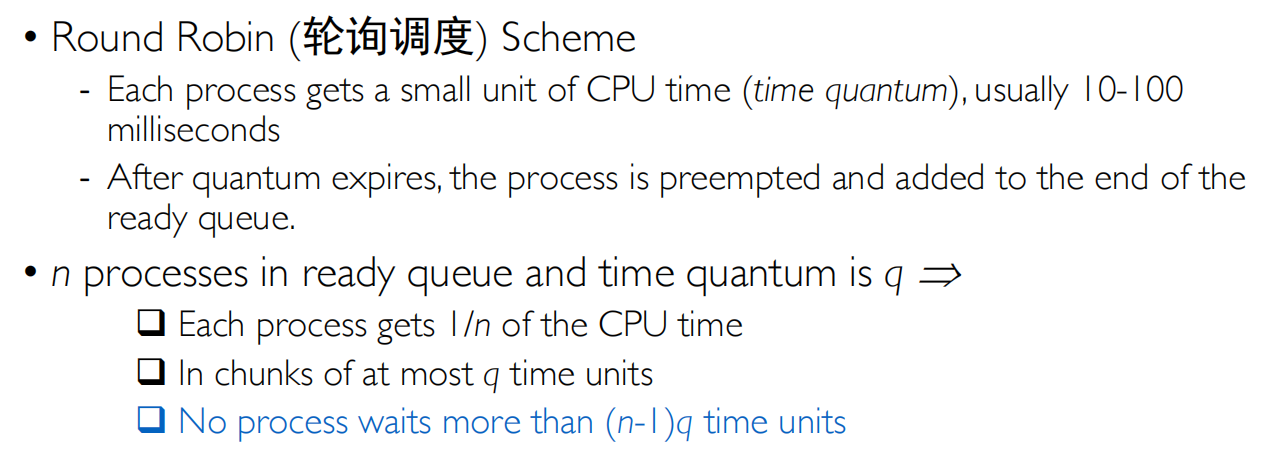
Round Robin(轮询调度) Scheme
每个任务得到CPU的一段时间,跑完之后重新放回队列中
-
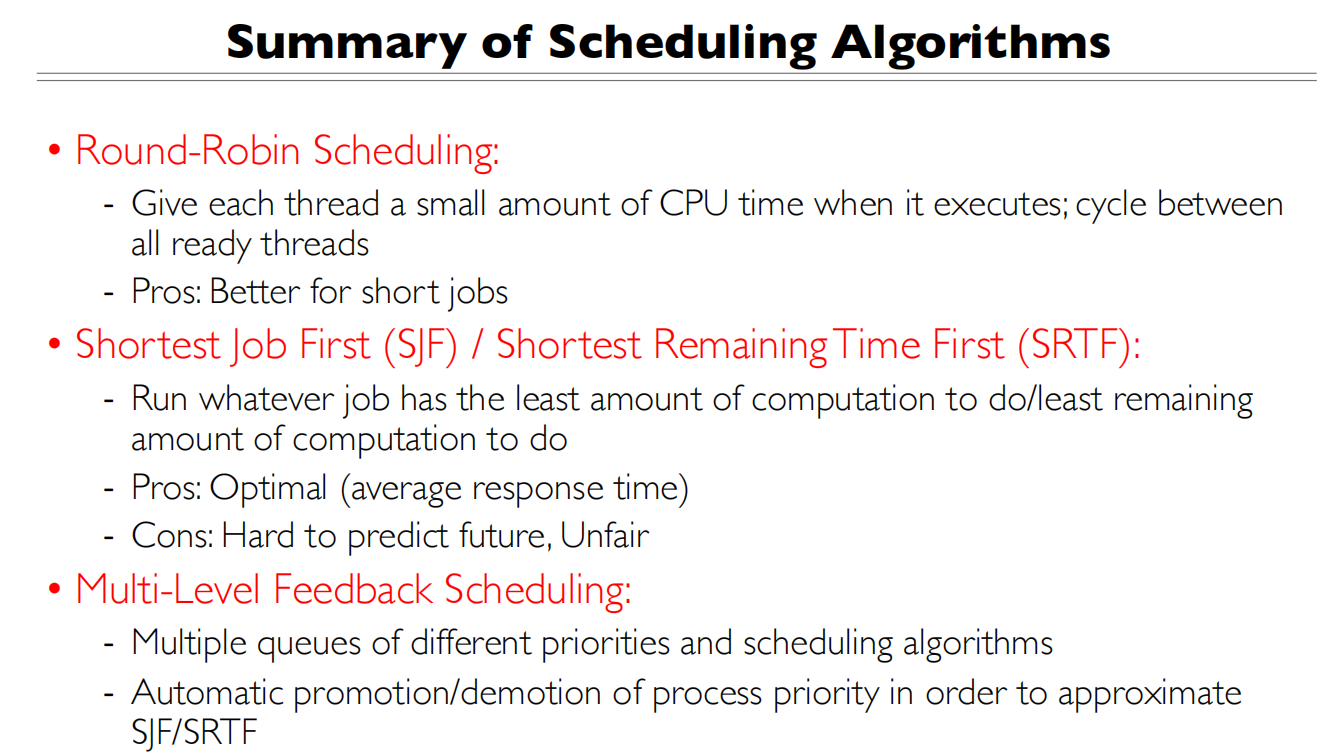
Thus, Round-Robin Pros and Cons:
- Better for shor t jobs, Fair (+)
- Context-switching time adds up for long jobs (-)
-
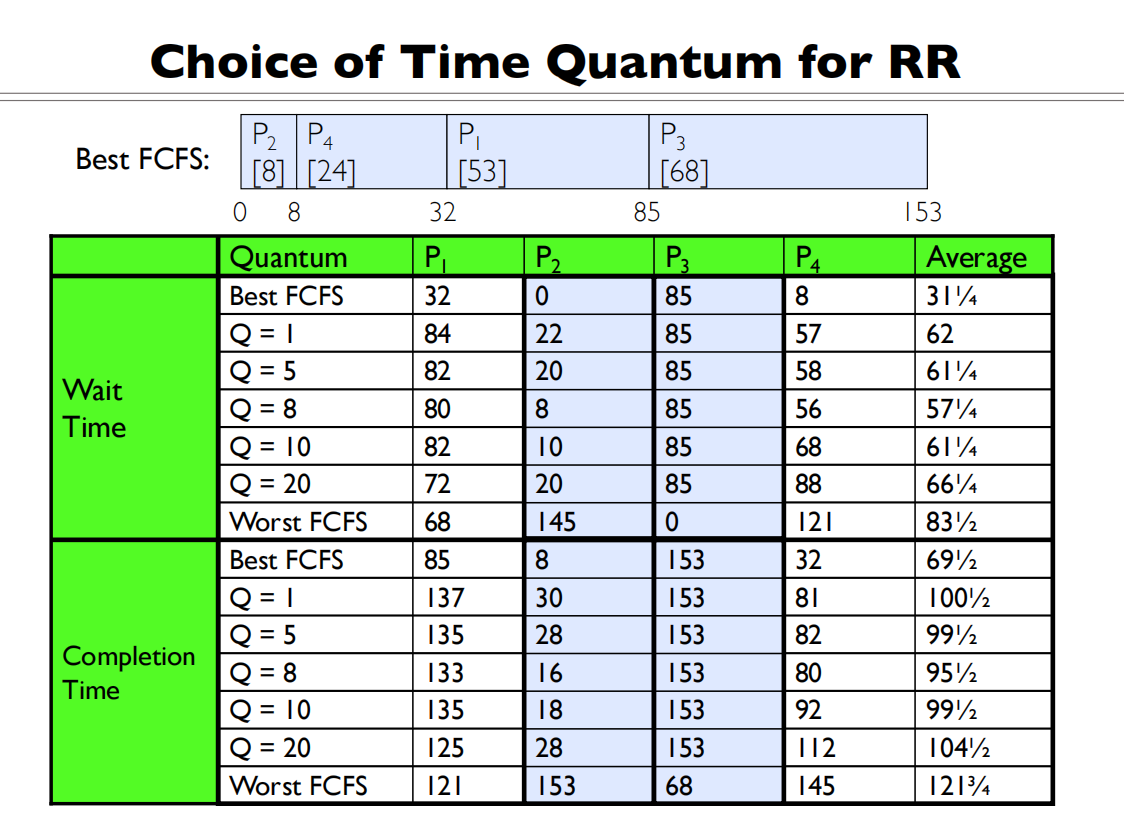
How do you choose time slice?
- Too large: Response time suffers
- What if infinite? Falls back to FIFO
- Too small: Throughput suffers
- Too large: Response time suffers
-
Actual choices of timeslice:
- Initially, UNIX timeslice one second:
- Worked ok when UNIX was used by one or two people.
- What if three compilations going on? 3 seconds to echo each keystroke!
- Need to balance short-job performance and long-job throughput:
- Typical time slice today is between 10ms – 100ms
- Typical context-switching overhead is 0.1ms – 1ms
- Roughly 1% overhead due to context-switching
- Initially, UNIX timeslice one second:
严格优先级调度
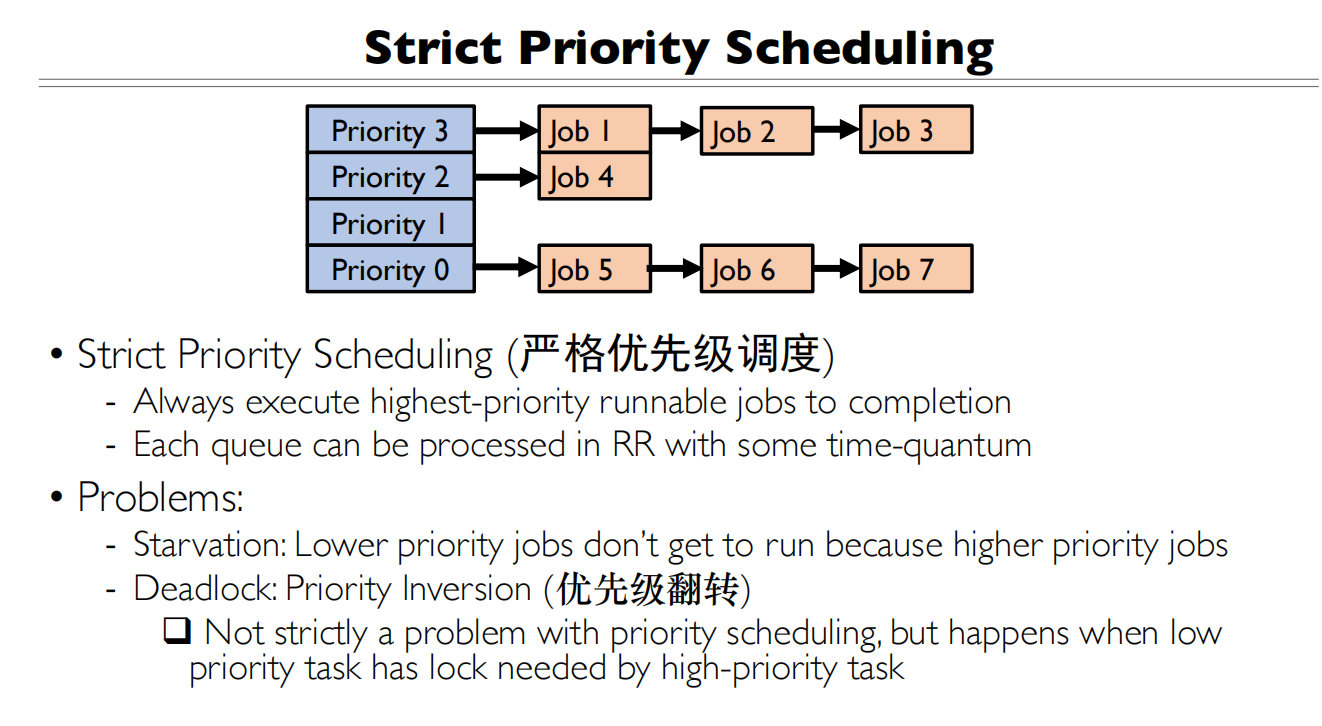
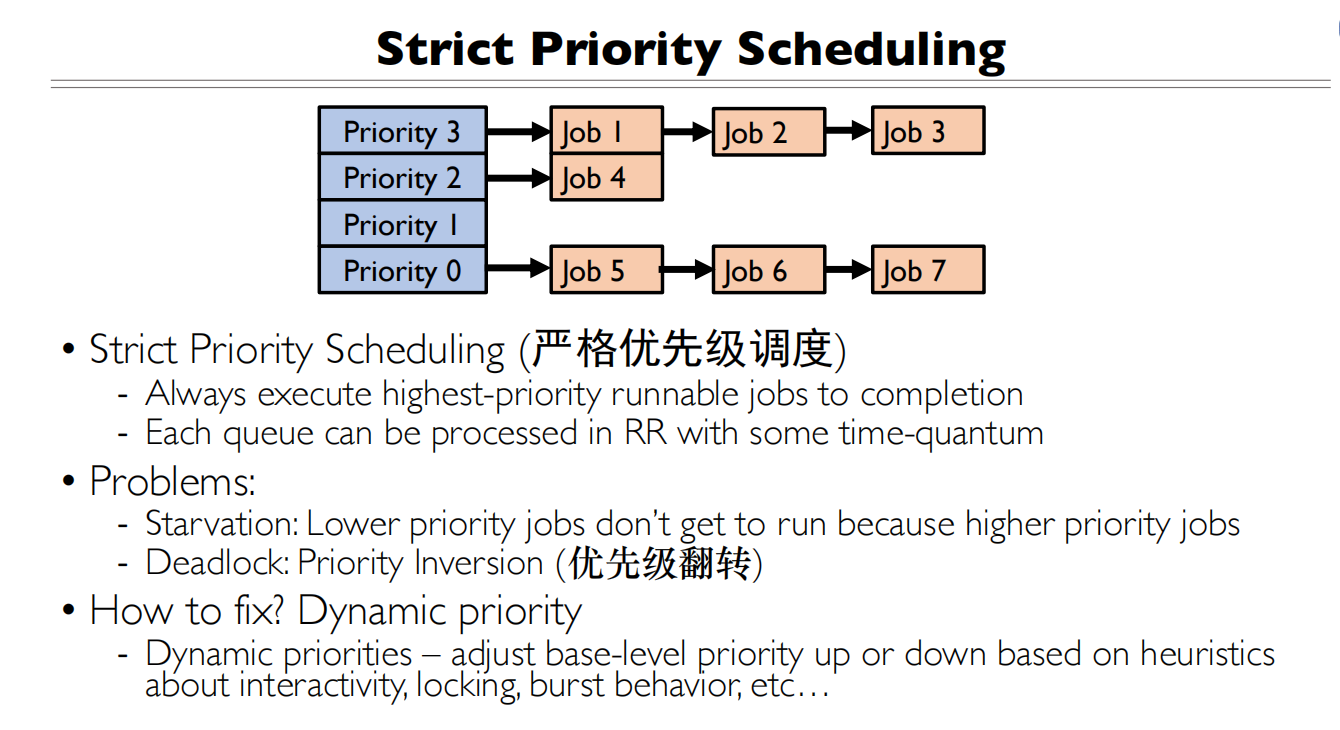 死锁会导致优先级反转,如何解决这个问题?
死锁会导致优先级反转,如何解决这个问题?
Earlises Deadline First(EDF)
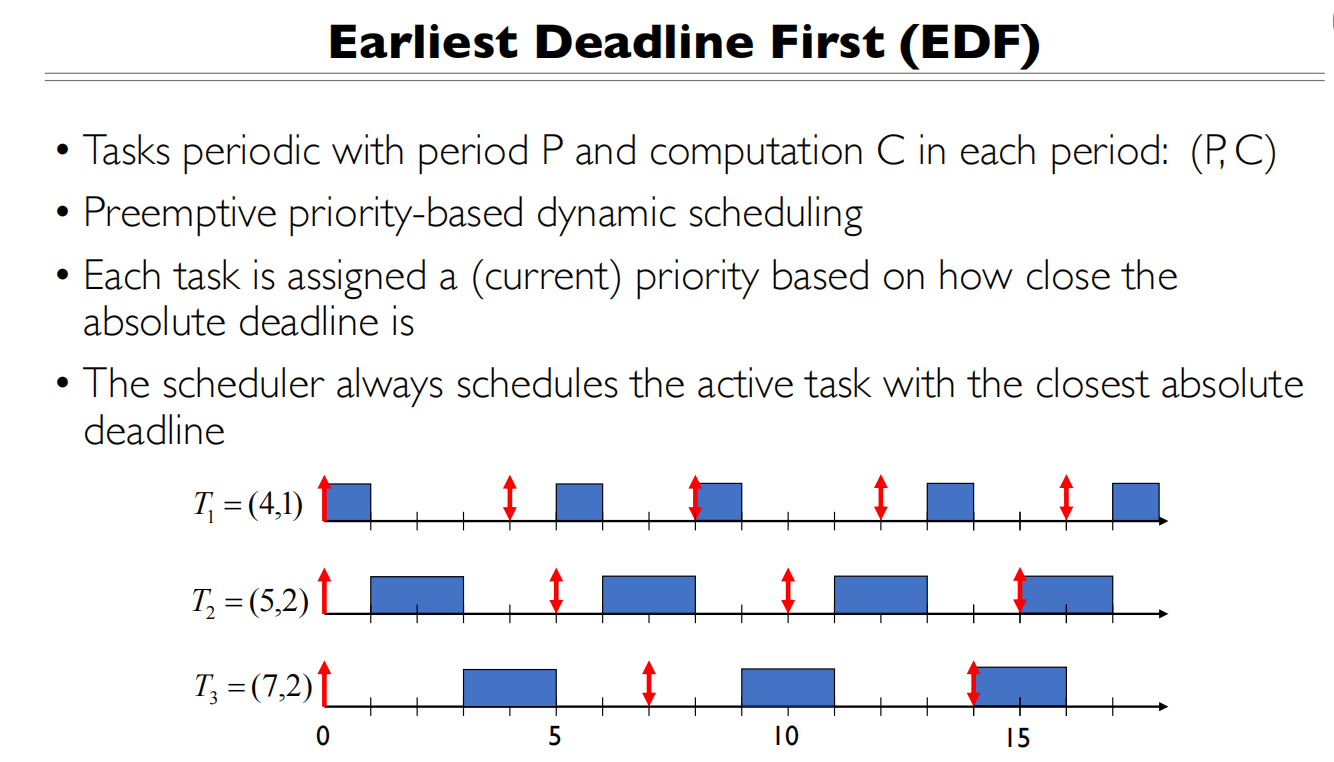
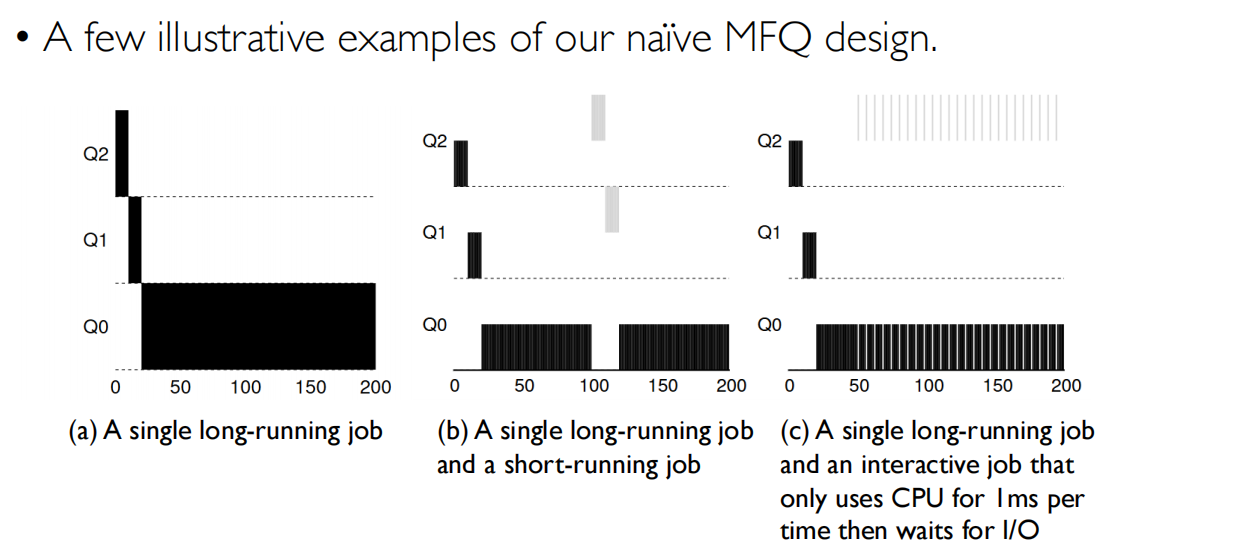
MFQ(多级反馈队列)
任务的需求不同:
- 高I/O:需要早点调度(鼠标点击等)
- 计算任务


 动态的优先级调度
动态的优先级调度
- 如果时间片用完了,优先级降1级
- 如果有I/O进入,则重新放到最优先级
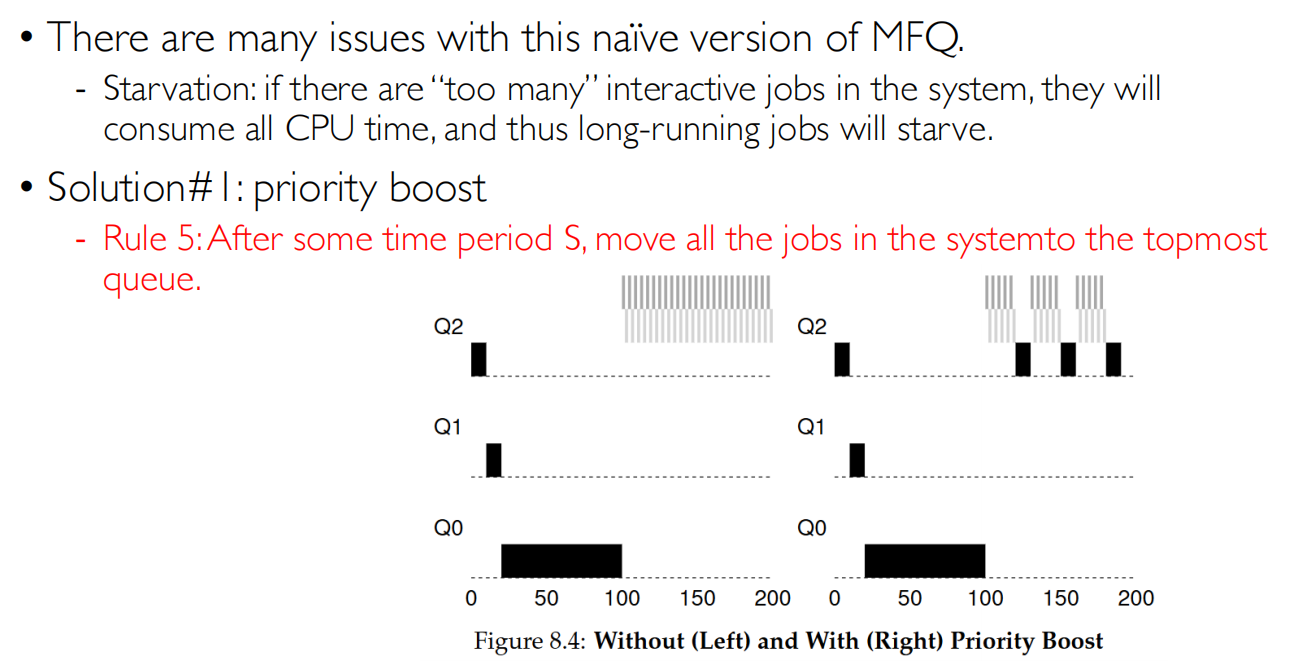 priority boost会引进新的参数
priority boost会引进新的参数
 不同优先级给不同的时间片大小
不同优先级给不同的时间片大小
 加一点I/O,伪装成高I/O的任务,多占据CPU时间
加一点I/O,伪装成高I/O的任务,多占据CPU时间
如何解决?
Tip
- 饥饿(Starvation)问题的解决:
实现老化(Aging)机制:定期提升长期等待进程的优先级
设置最长等待时间阈值,超过阈值强制提升优先级
在较低优先级队列增加时间片长度,让CPU密集型任务也能得到充分执行
- 针对用户滥用I/O操作提高优先级的对策:
实现I/O操作计数器,监控进程的I/O行为
当检测到异常频繁的I/O操作时,不提升或降低其优先级
区分真实I/O和虚假I/O操作,只对真实I/O做优先级奖励
- 调度器参数优化:
队列数量:通常设置3-8个级别,根据系统负载特征调整
时间片大小:
- 高优先级队列使用较短时间片(如20ms)
- 低优先级队列使用较长时间片(如100ms-200ms)
- 可以根据实际工作负载动态调整
实现动态调整机制,根据系统性能指标自适应调整参数
- 其他改进:
- 引入优先级提升窗口,限制提升频率
- 实现优先级继承,避免优先级反转
- 加入负载均衡机制,防止某个优先级队列过载
- 支持优先级预设,让系统管理员可以为特定应用设置合理的优先级范围
 更高优先级的队列,时间片应该更小,以便于更快地响应高优先级的任务
更高优先级的队列,时间片应该更小,以便于更快地响应高优先级的任务
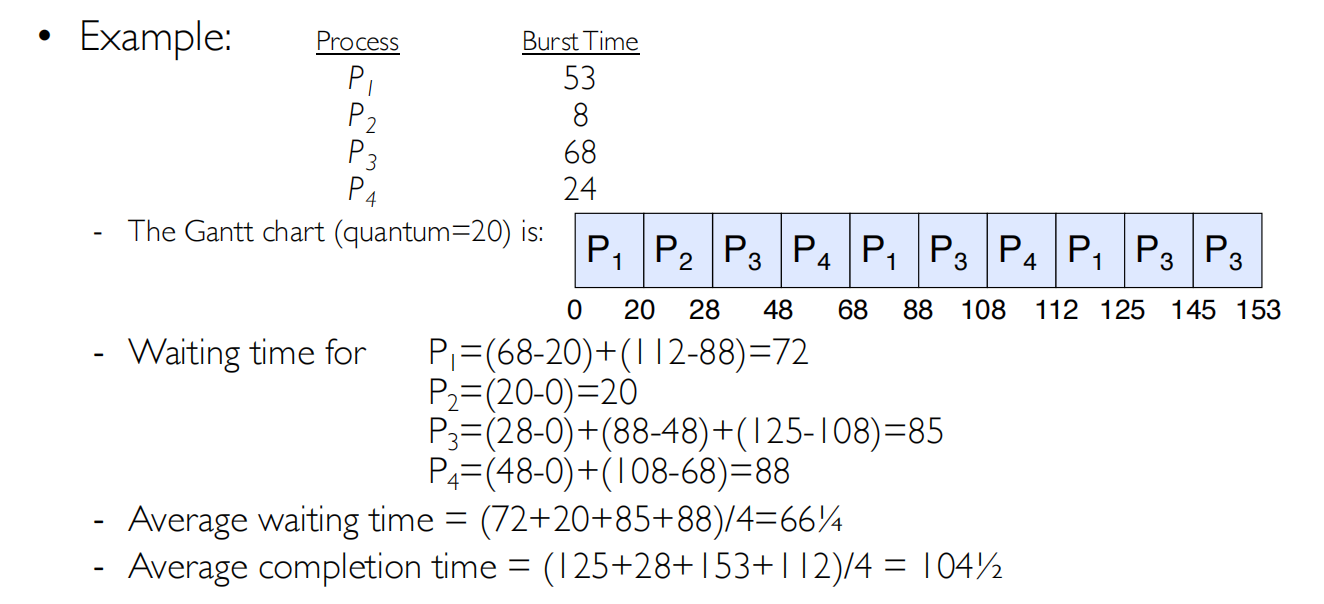
例子
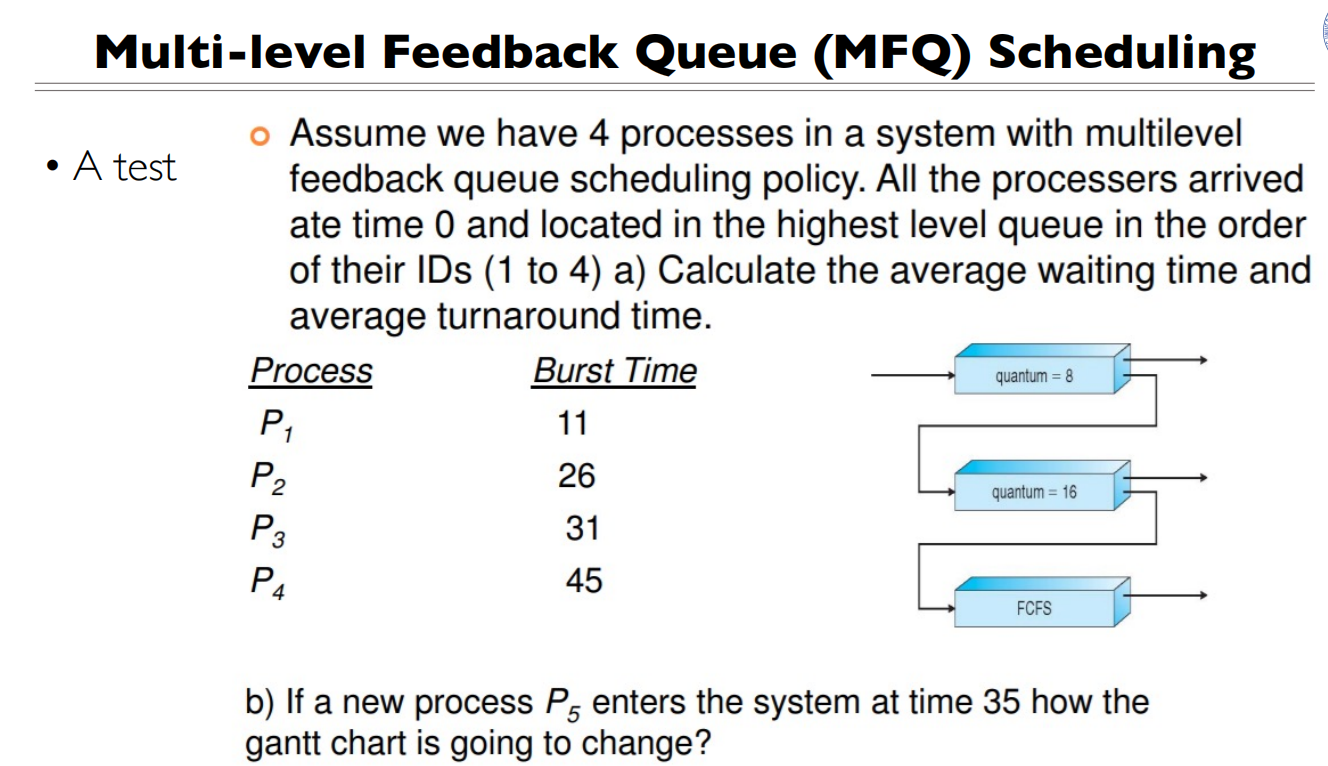 等待时间=完成时间-所要运行的时间
等待时间=完成时间-所要运行的时间
Lottery Scheduling
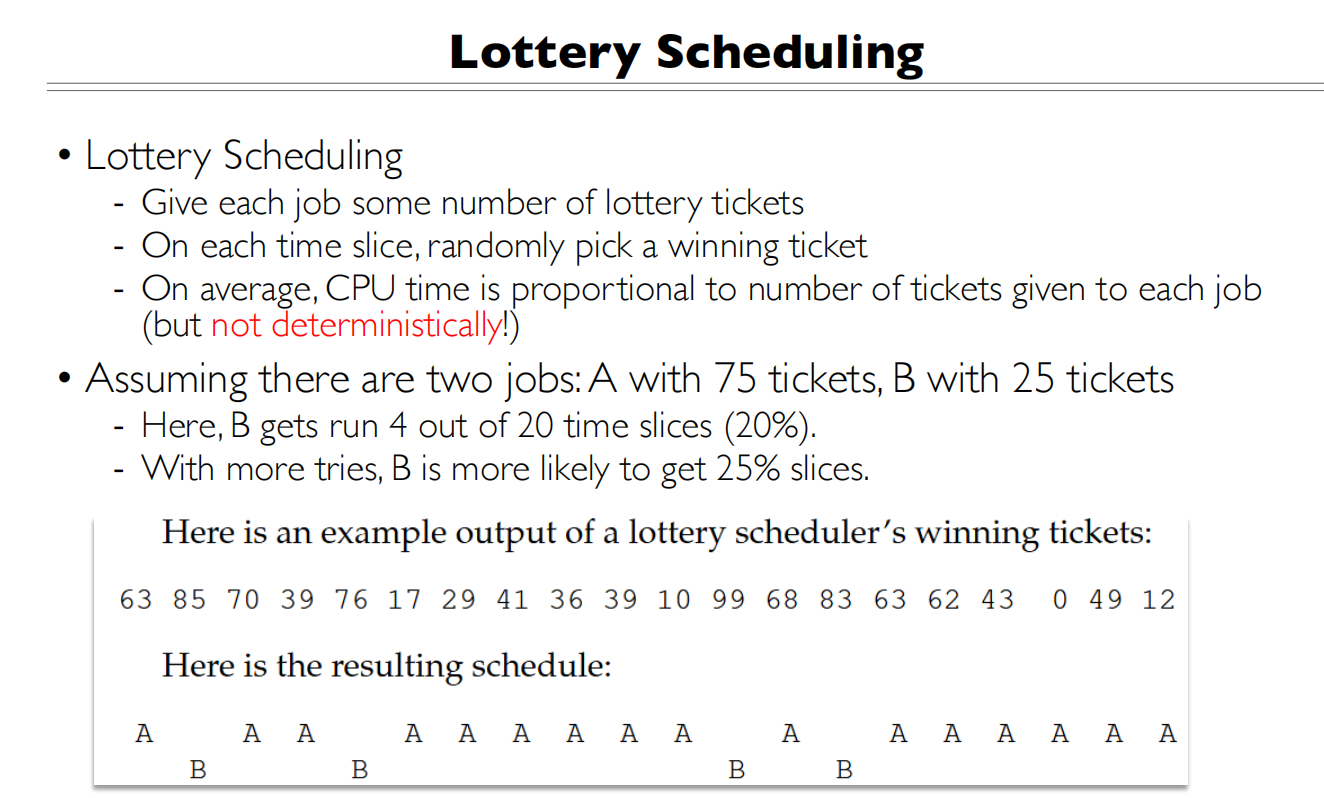 每个任务拥有的彩票在统计意义上和调度时间正比,但并不完全正比(大数定理)
每个任务拥有的彩票在统计意义上和调度时间正比,但并不完全正比(大数定理)
 实现很简单,而且当一个新任务加入/旧任务丢弃,会影响到其他的任务
实现很简单,而且当一个新任务加入/旧任务丢弃,会影响到其他的任务
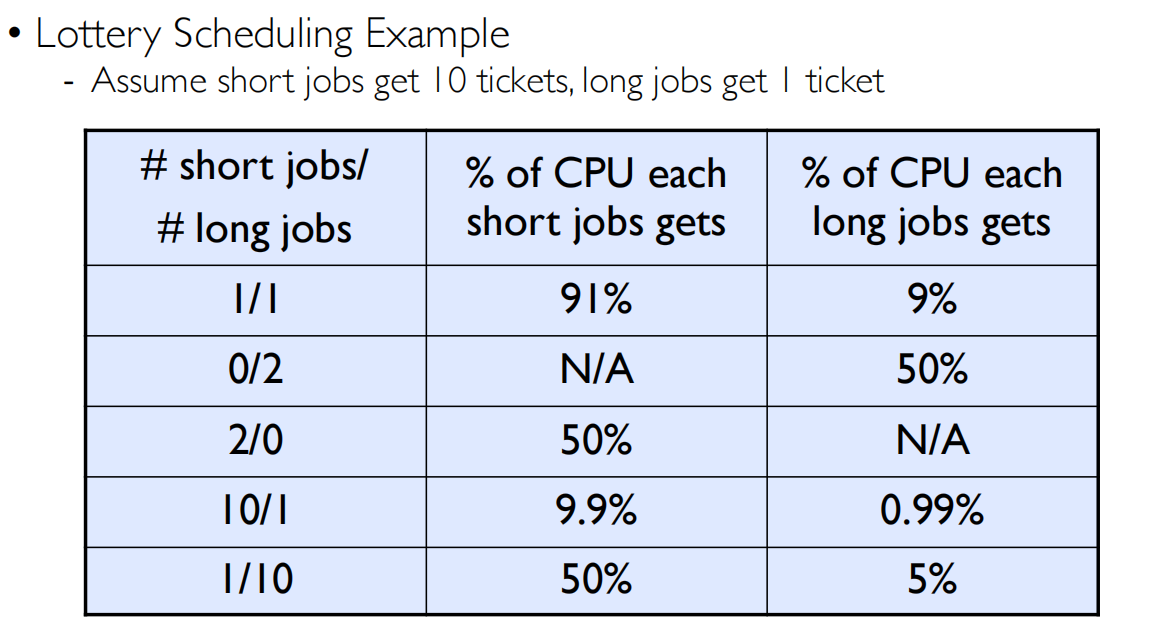
- Implementing lottery scheduling is amazingly easy!
- One of the impor tant feature of it.
- You only need
- A good random number generator(随机数生成器)
- A data structure to track the processes of the system and the total number of tickets (链表)
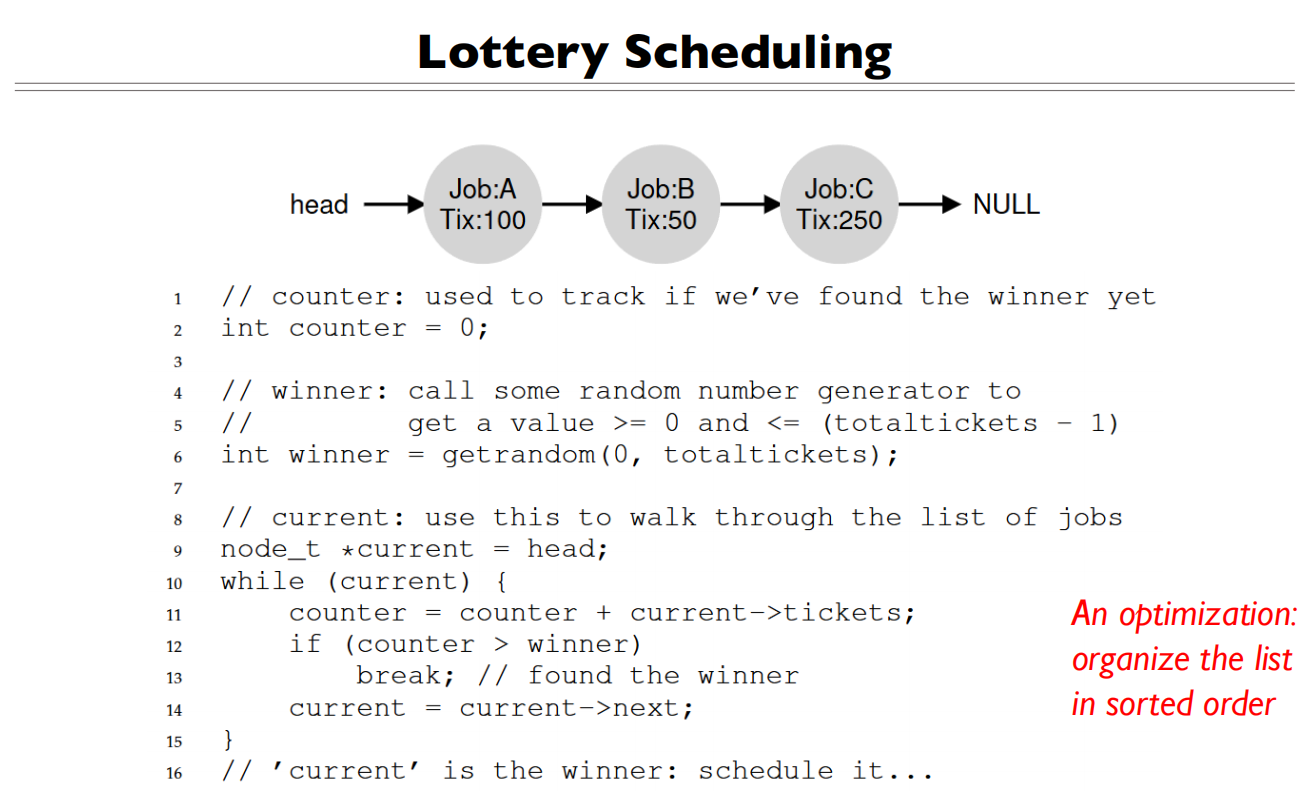 优先级排序,可以将彩票数多的放在前面,链表遍历的节点数会变少
优先级排序,可以将彩票数多的放在前面,链表遍历的节点数会变少
CFS
 目的是让每个任务都获得比较公平的调度
目的是让每个任务都获得比较公平的调度
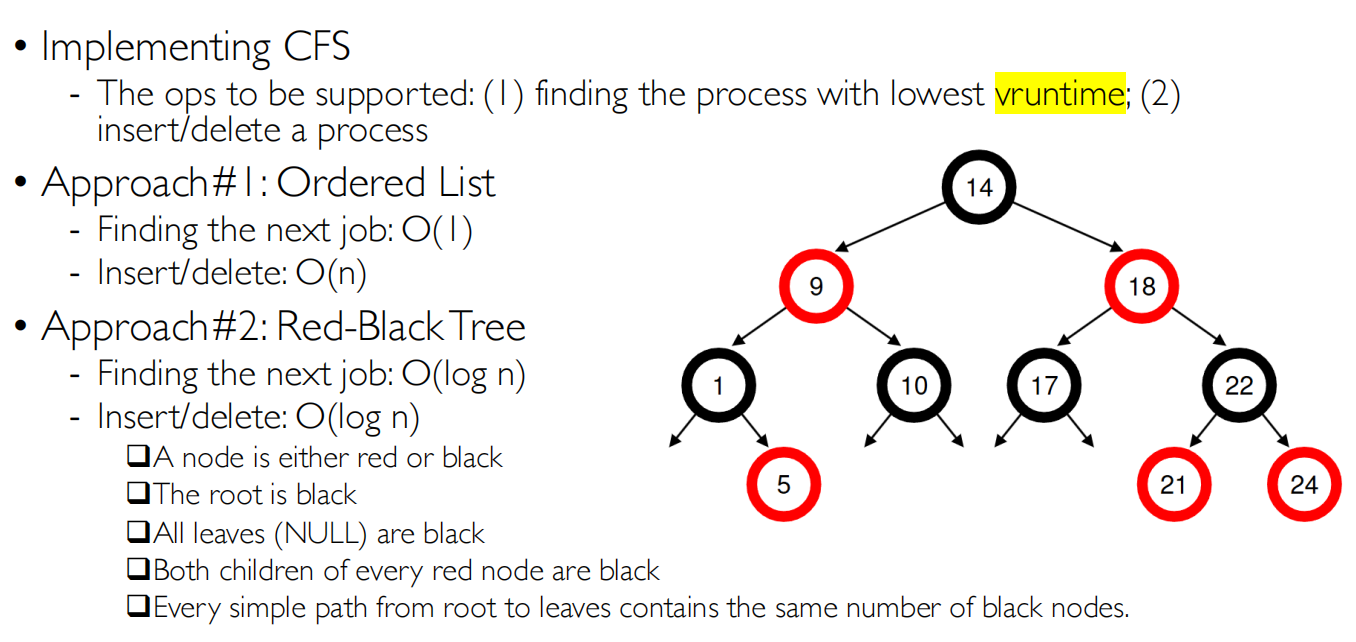
Max-Min思想,每次选择一个vruntime 最小的任务调度
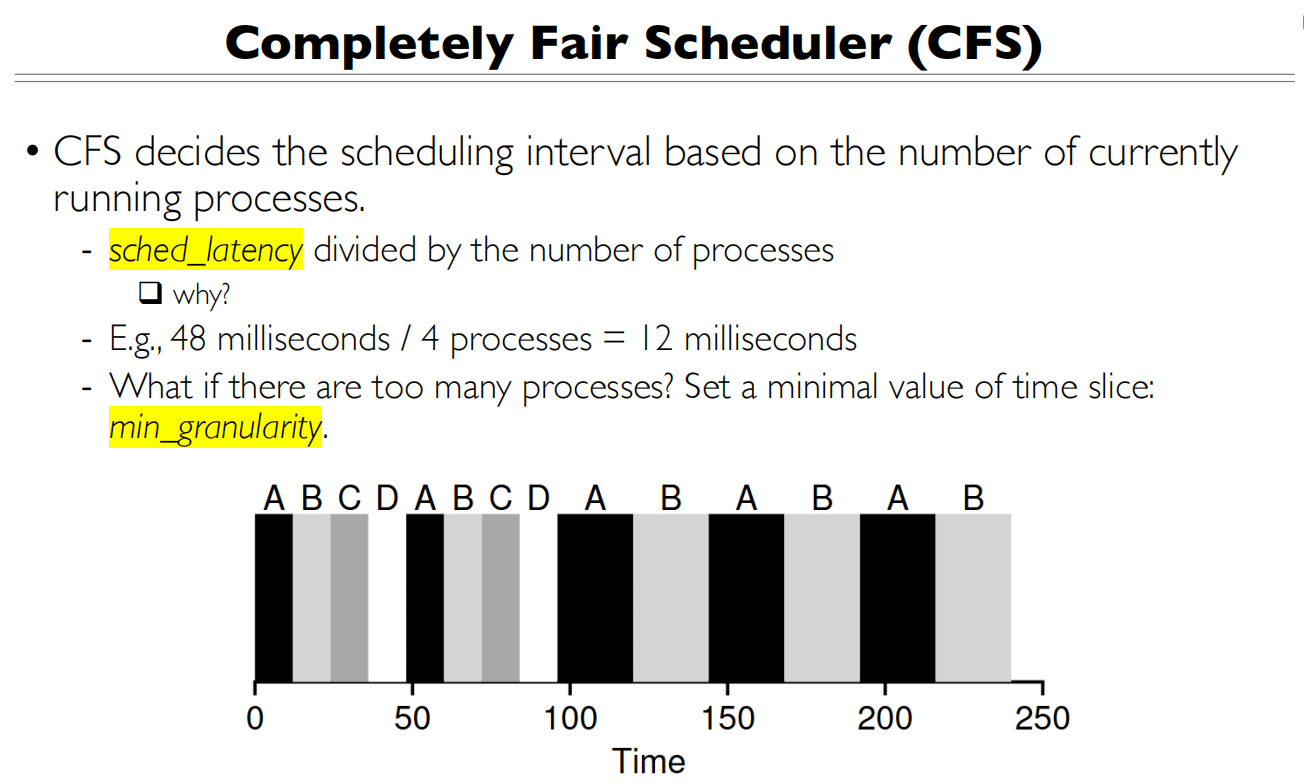 48是一个调度的周期,有4个任务,那么就是48/4=12 milliseconds。任务越多,调度的时间片越短
48是一个调度的周期,有4个任务,那么就是48/4=12 milliseconds。任务越多,调度的时间片越短
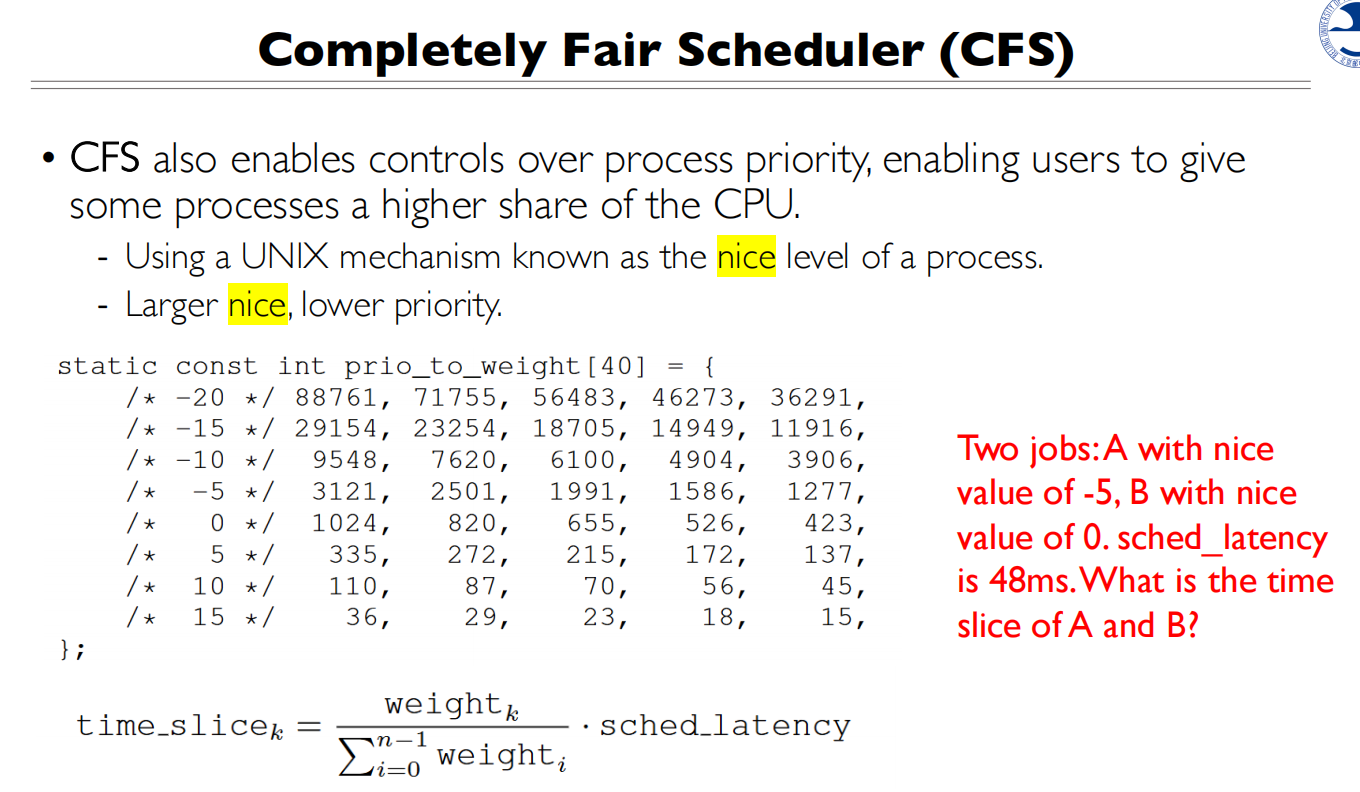 nice值可以认为是优先级,nice值越高,优先级越低
nice值可以认为是优先级,nice值越高,优先级越低
 这两个Case的调度是一样的,所以和nice值的绝对值无关,和相对值有关
这两个Case的调度是一样的,所以和nice值的绝对值无关,和相对值有关
优先级越高,获得的时间片越多;高优先级进程的vruntime增长较慢
RTS
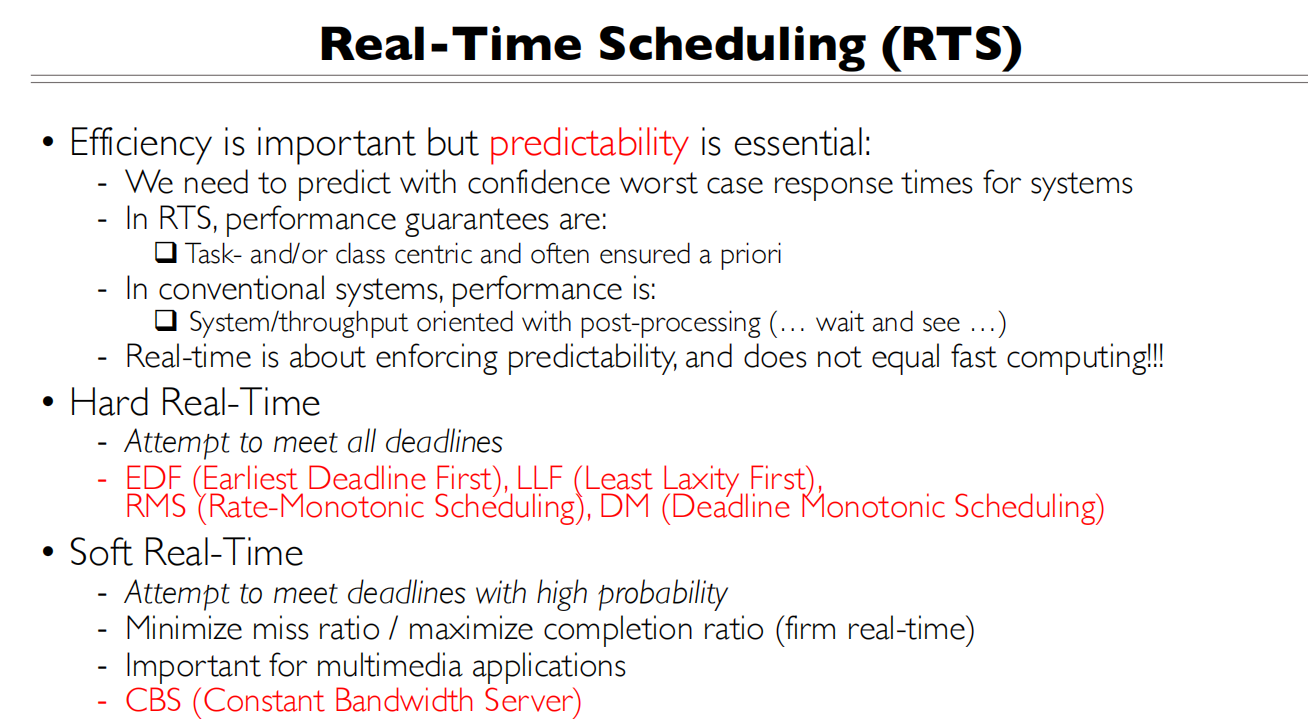 最重要的不是快,而是确定性
最重要的不是快,而是确定性
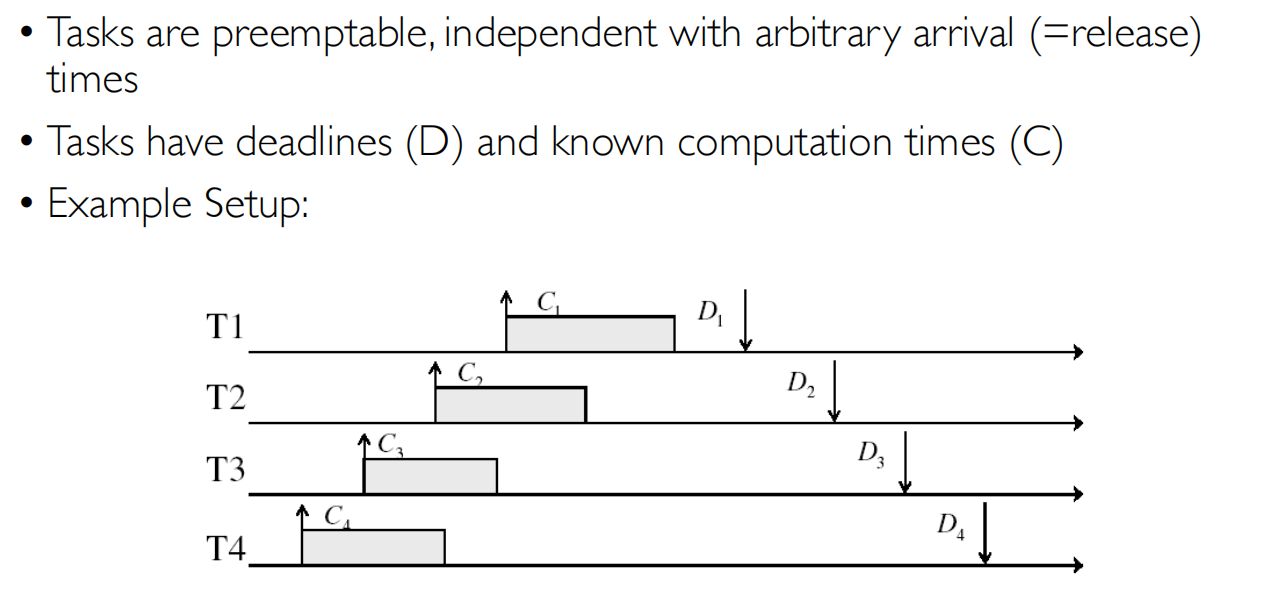
多处理器调度
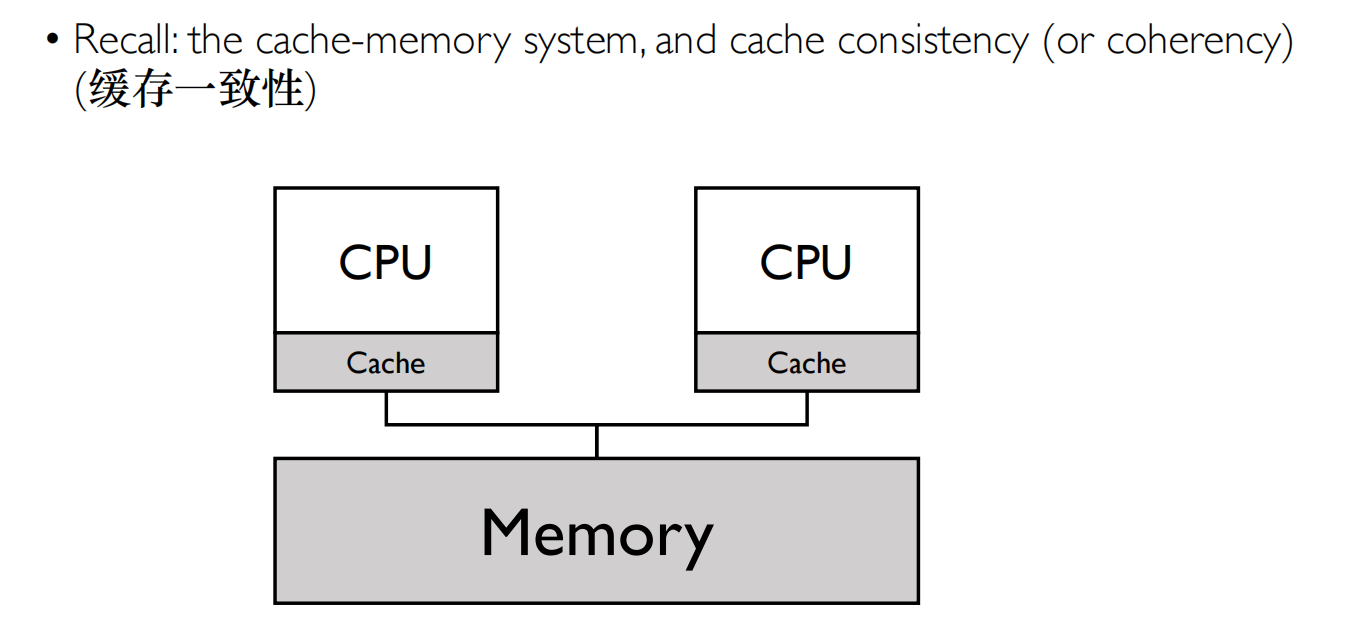
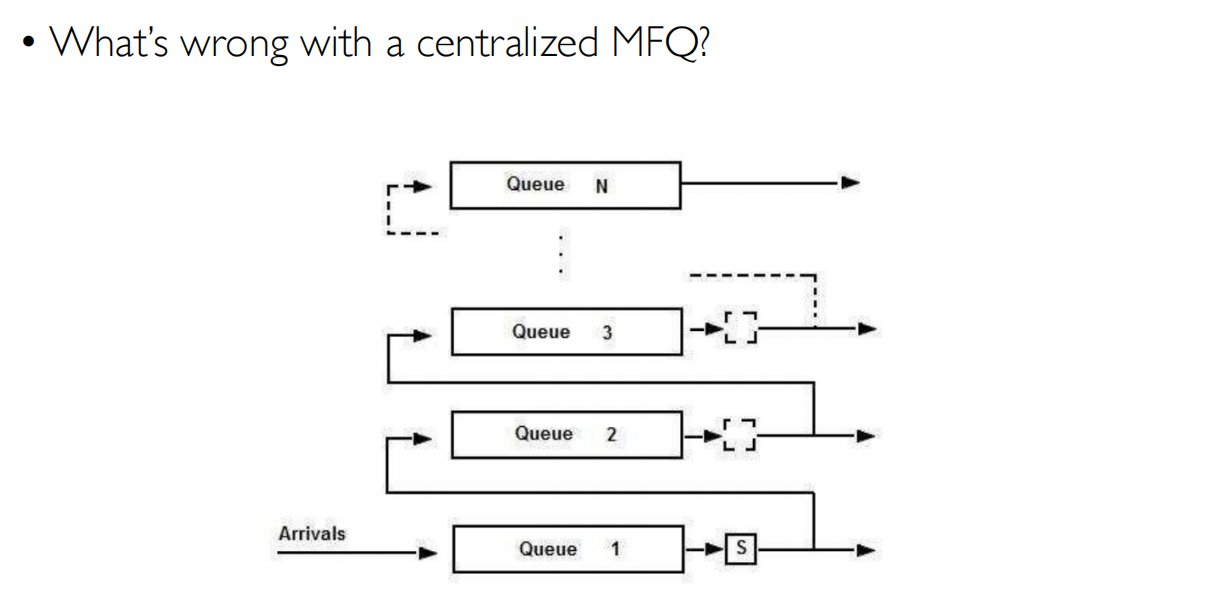 共享一个MFQ
共享一个MFQ
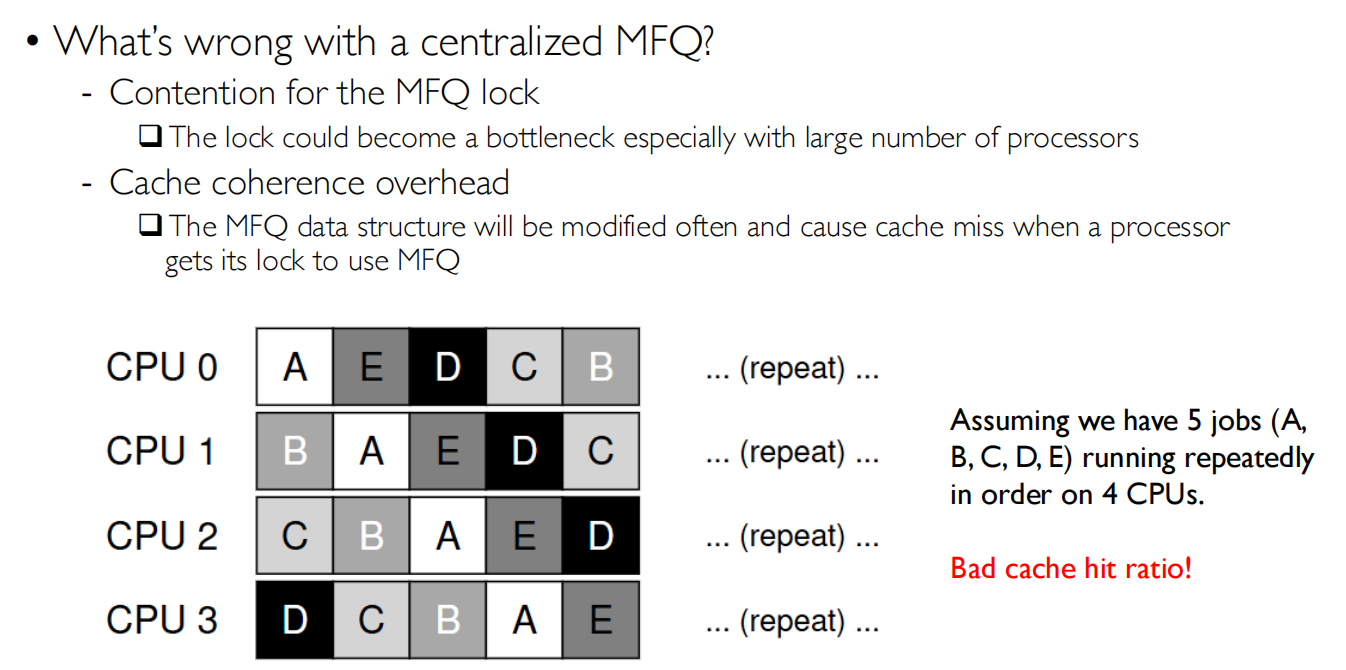
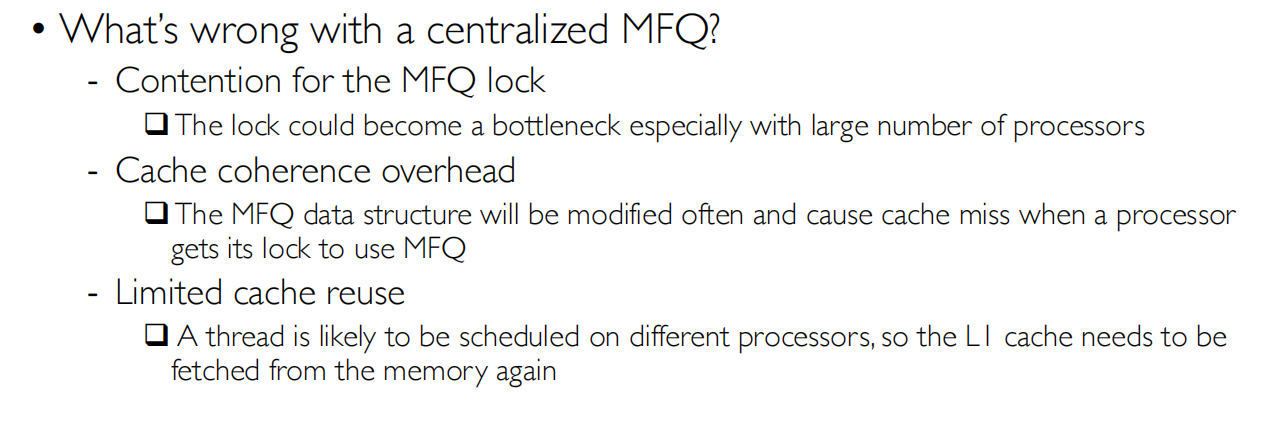 同步的问题,缓存命中率的问题
同步的问题,缓存命中率的问题
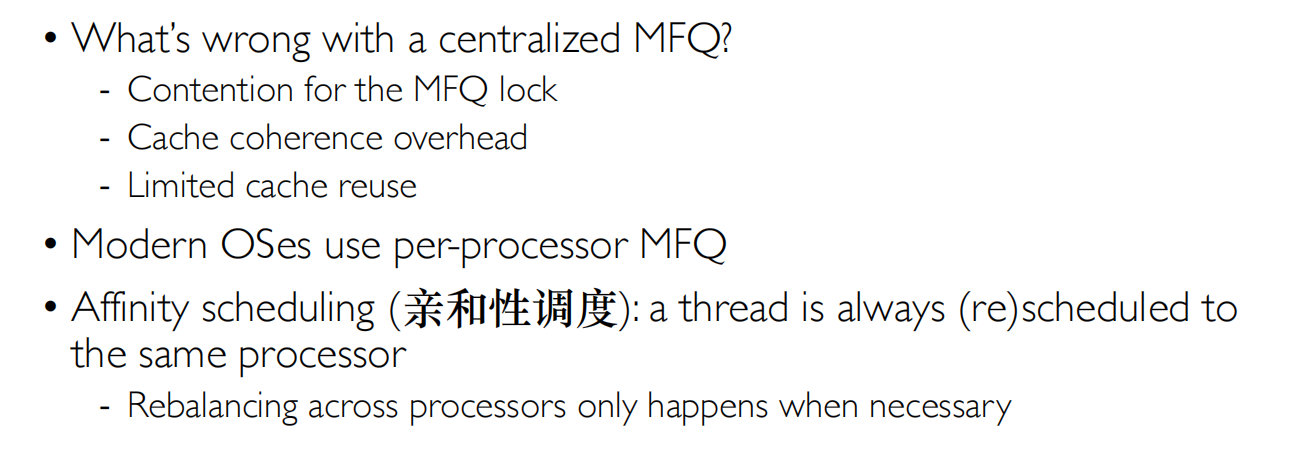

Summary